Trisomie 21 Nondisjunction
Http Www Scielo Org Co Pdf Sun V26n1 V26n1a12 Pdf
Q Tbn And9gcqacztp1suhvyd6fktmemzln Bpjkk8vecfwbw4bp2lnjb9eiao Usqp Cau

Pdf Mosaicism For Trisomy 21 A Review

Chromosome 21 An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Chromosome Trisomy Disease Malacards Research Articles Drugs Genes Clinical Trials
Genetik Morphologie Menschlicher Chromosomen Chromosomenzahlaberration
Peterson MB, Mikkelsen M Nondisjunction in trisomy 21 origin and mechanisms Cytogenet Cell Genet 00 Down JL Observations on an ethnic classification of idiots 1866 Ment Retard 1995 Feb 33(1)546 LEJEUNE J, GAUTIER M, TURPIN R Study of somatic chromosomes from 9 mongoloid children.

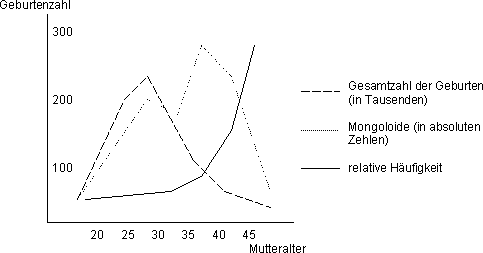
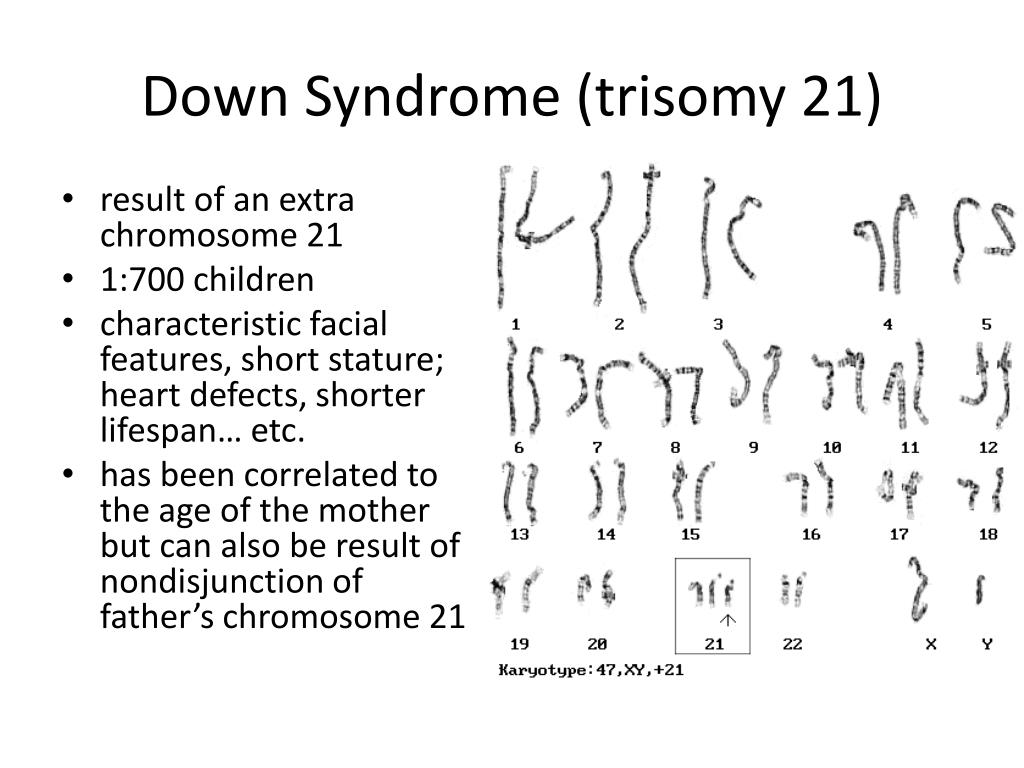
Trisomie 21 nondisjunction. Down syndrome is an anomaly of chromosome 21 that can cause intellectual disability, microcephaly, short stature, and characteristic facies Diagnosis is suggested by physical anomalies and abnormal development and confirmed by cytogenetic analysis Management depends on specific manifestations and anomalies. Down syndrome (trisomy 21 or DS) is a group of signs, symptoms, and health problems that arise from an error in cell division that results in an extra chromosome 21 This may occur before or shortly after conception and has a widespread effect on the physical and intellectual development of the affected person. Somies 21 (Down Syndrome), 18 (Edward's Syndrome) or 13 (Patou Syndrome) increases with the mother's age (Valero et al, 1999) According to Pena (1998), in trisomy 21, the increase in the rate of nondisjunction in meiosis II is higher than for meiosis I if the mother's age is between 35 and 39 years For sexual chromo.
Approximately 2% of spontaneous abortions and 1% of stillbirths will have trisomy 21. Approximately 2% of spontaneous abortions and 1% of stillbirths will have trisomy 21. Stene J (1981) Effect of advancing paternal age on the incidence of trisomy 21 In Burgio GR, Fraccaro M, Tiepolo I, Wolf U (eds) Trisomy 21 Human Genetics, Supplement 2 Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 257–258 Google Scholar.
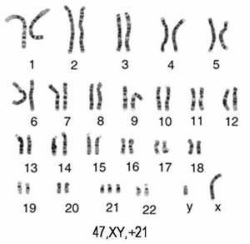
The Qband heteromorphisms of chromosome 21 were used in a sample of 48 families with a Down's syndrome child to evaluate the origin of nondisjunction The parental origin and the meiotic error. Trisomy 21 (also known by the karyotype 47,XX,21 for females and 47,XY,21 for males) is caused by a failure of the 21st chromosome to separate during egg or sperm development (nondisjunction) As a result, a sperm or egg cell is produced with an extra copy of chromosome 21;. Down syndrome is an anomaly of chromosome 21 that can cause intellectual disability, microcephaly, short stature, and characteristic facies Diagnosis is suggested by physical anomalies and abnormal development and confirmed by cytogenetic analysis Management depends on specific manifestations and anomalies.
Once a woman has given birth to a baby with trisomy 21 (nondisjunction) or translocation, it is estimated that her chances of having another baby with trisomy 21 is 1 in 100 up until age 40 The risk of recurrence of translocation is about 3% if the father is the carrier and 1015% if the mother is the carrier. The reported frequency for double trisomy cases ranges from 021 to 28% in studies not restricted to first trimester abortions Our frequency is therefore within the reported range in other studies A survey performed by Guerneri et al (1987) of 2 first trimesteronly loss villus samples found double trisomy in 58% of the cases. What is Down syndrome?.
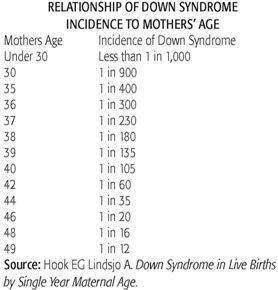
Down syndrome (trisomy 21) is the most commonly recognized genetic cause of mental retardation The risk of trisomy 21 is directly related to maternal age All forms of prenatal testing for Down. 23 (Suppl)1–30 Google ScholarLicznerski G, Lindsten J Trisomy 21 in man due to maternal nondisjunction during the first meiotic division. In trisomy 21, the presence of an extra set of genes leads to overexpression of the involved genes, leading to increased production of certain products For most genes, their overexpression has little effect due to the body's regulating mechanisms of genes and their products But the genes that cause Down syndrome appear to be exceptions.
In addition to environmental factors, various genetic factors have been described which seem to influence the nondisjunction rate during meiosis The first data of DS in the Oman yielded a high prevalence among live births The birth prevalence of Trisomy 21 in Oman with 1454 newborns is, perhaps, the highest reported so far. Our project for Advanced Genetics (in Arcadia's Genetic Counseling program)A brief stopmotion walkthrough of nondisjunction during Meiosis IIRed Twizzlers. Full trisomy 21 and mosaicism are not inherited, but originate from errors in cell divisions during the development of the egg, sperm or embryo In addition, full trisomy for chromosome 21 should be further divided into cases of maternal origin, the majority, and cases of paternal origin, less than 10 %.
Down syndrome (trisomy 21) is the most commonly recognized genetic cause of mental retardation The risk of trisomy 21 is directly related to maternal age All forms of prenatal testing for Down. Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) is the most common chromosomal abnormality amongst livebirths, with an incidence of 1/800 It is estimated that 80% of all trisomy 21 pregnancies conceived end as spontaneous abortions or as stillbirths;. A free trisomy 21 results from nondisjunction during meiosis in one of the parents;.
Inici > Veure vídeos > Cuina i Salut > Salut > Trisomy 21 Nondisjunction Trisomy 21 Nondisjunction Compartir a 5515 0 comentaris Categoria Cuina i Salut Trisomie 21 La Brosse à Dents Veure vídeo Veure tots els vídeos de "Salut" PATROCINADORS COL·LABORADORS. Somies 21 (Down Syndrome), 18 (Edward's Syndrome) or 13 (Patou Syndrome) increases with the mother's age (Valero et al, 1999) According to Pena (1998), in trisomy 21, the increase in the rate of nondisjunction in meiosis II is higher than for meiosis I if the mother's age is between 35 and 39 years For sexual chromo. Inici > Veure vídeos > Cuina i Salut > Salut > Trisomy 21 Nondisjunction Trisomy 21 Nondisjunction Compartir a 5515 0 comentaris Categoria Cuina i Salut Trisomie 21 La Brosse à Dents Veure vídeo Veure tots els vídeos de "Salut" PATROCINADORS COL·LABORADORS.
The term "trisomy" is used to describe the presence of an extra chromosome — or three instead of the usual pair For example, trisomy 21 or Down syndrome occurs when a baby is born with three #21 chromosomes In trisomy 18, there are three copies of chromosome #18 in every cell of the body, rather than the usual pair. This occurrence is correlated with advanced maternal and paternal age Translocation Translocation occurs when genetic material from chromosome 21 becomes attached to another chromosome, resulting in 46 chromosomes, with 1 chromosome having extra material from. What is Down syndrome?.
Trisomy 9 is a rare disorder in which a full trisomy is usually fatal within the first 21 days of life Newborns with trisomy 9 will have a smaller head, distinctive facial features (including a bulbous nose and sloping forehead), a deformed heart, kidney problems, and often severe muscle and skeletal malformations. (3) Maternal meiosis II errors constitute to 24% of maternal errors and 18 to % of all cases of free trisomy 21 The mean maternal age is also advanced and is 314 in one study and 341 in another (4) In rare families in which there is paternal nondisjunction, most of the errors occur in meiosis II. Down syndrome (trisomy 21 or DS) is a group of signs, symptoms, and health problems that arise from an error in cell division that results in an extra chromosome 21 This may occur before or shortly after conception and has a widespread effect on the physical and intellectual development of the affected person.
Down syndrome is by far the most common and best known chromosomal disorder in humans and the most common cause of intellectual disability It is primarily caused by trisomy of chromosome 21 (see. Down syndrome (trisomy 21) is a genetic disorder It includes certain birth defects, learning problems, and facial features A child with Down syndrome also may have heart defects and problems with vision and hearing A mother’s age at her child’s birth is the only factor linked to the risk of having a baby with Down syndrome. Somies 21 (Down Syndrome), 18 (Edward's Syndrome) or 13 (Patou Syndrome) increases with the mother's age (Valero et al, 1999) According to Pena (1998), in trisomy 21, the increase in the rate of nondisjunction in meiosis II is higher than for meiosis I if the mother's age is between 35 and 39 years For sexual chromo.
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) is the most common chromosomal abnormality amongst livebirths, with an incidence of 1/800 It is estimated that 80% of all trisomy 21 pregnancies conceived end as spontaneous abortions or as stillbirths;. Approximately 2% of spontaneous abortions and 1% of stillbirths will have trisomy 21. Trisomy 21 has a wide range of distinctive symptoms from external characteristics to developmental delays Children with trisomy 21 have broad, wide faces with eyes that slant upwards They have reduced nasal bridges, short noses and small palms with short fingers There is usually a large gap between their big toe and second toe.
Licznerski G, Lindsten J Trisomy 21 in man due to maternal nondisjunction during the first meiotic division. Down syndrome (DS), characterized by an extra free chromosome 21 is the most common genetic cause for congenital malformations and learning disability It is well known that the extra chromosome 21 originates from the mother in more than 90% of cases, the incidence increases with maternal age and there is a high recurrence in young women. Also known as Down syndrome, trisomy 21 is a genetic condition caused by an extra chromosome Most babies inherit 23 chromosomes from each parent, for a total of 46 chromosomes Babies with Down syndrome however, end up with three chromosomes at position 21, instead of the usual pair Other examples of trisomies occur at position 13 and 18.
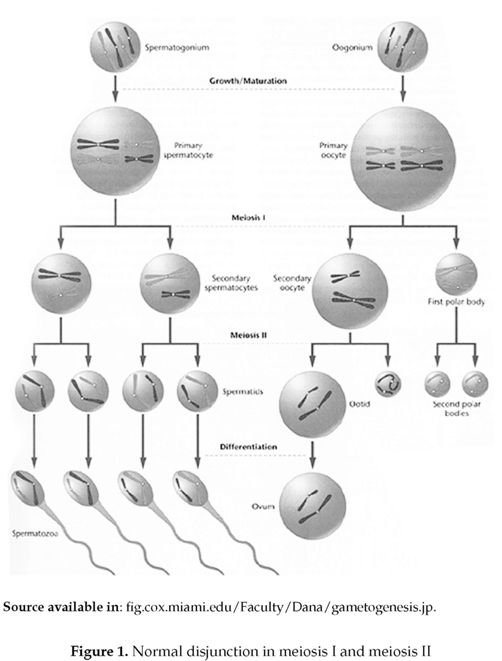
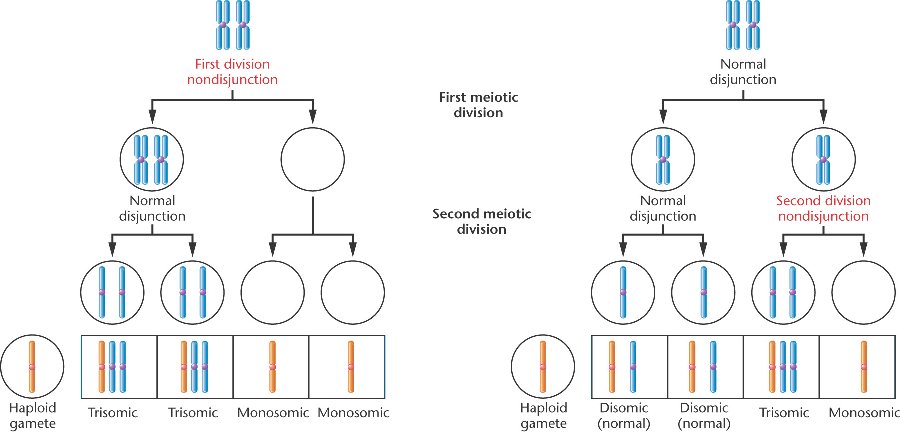
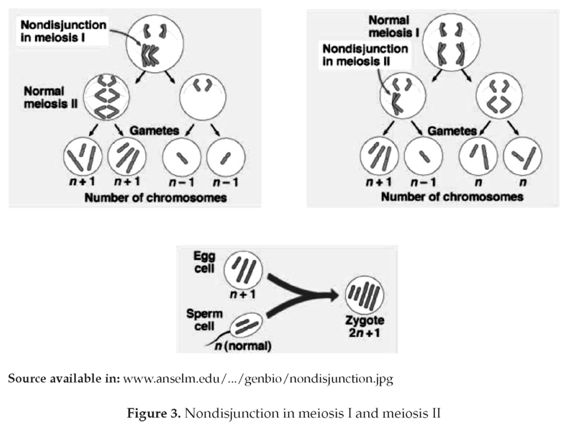
1 Cytogenet Genome Res 05;111(34) Risk factors for nondisjunction of trisomy 21 Sherman SL(1), Freeman SB, Allen EG, Lamb NE Author information (1)Department of Human Genetics, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA , USA ssherman@geneticsemoryedu The leading cause of Down syndrome (DS) is nondisjunction of chromosome 21 occurring during the formation of gametes. This cell thus has 24 chromosomes. Giraud F, Mattei JF Aspects epidémiologiques de la trisomie 21 J Genet Hum 1975 Oct;.
(3) Maternal meiosis II errors constitute to 24% of maternal errors and 18 to % of all cases of free trisomy 21 The mean maternal age is also advanced and is 314 in one study and 341 in another (4) In rare families in which there is paternal nondisjunction, most of the errors occur in meiosis II. Trisomy 21 is caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21 in every cell of the body in the majority of cases (94%) Around 3% of cases are due to mosaicism, and 3% are due to robertsonian. Amniotic fluid karyotyping showed nonmosaic trisomy 21 in twin 1 (47, XY, 21) and a normal karyotype in twin 2 (46, XY) Short tandem repeat (STR) polymorphism markers revealed that the two fetuses were monozygotic, and the two chromosomes 21 were maternal isodisomy in the trisomy fetus.
Autosomale Trisomien umfassen Trisomie 21 oder DownSyndrom, Trisomie 18 oder EdwardsSyndrom und Trisomie 13 oder PatauSyndrom Trisomien von Chromosomen neben Geschlechtschromosomen oder Chromosomen 13, 18 oder 21 führen fast immer zu Fehlgeburten Die Ausnahme ist der Mosaikismus, bei dem das Vorhandensein normaler Zellen die trisomischen. Trisomy 21 – More than 90% of Down syndrome cases are caused by trisomy 21 An extra chromosome (chromosome 21) originates in the development of either the sperm or the egg When the egg and the sperm unite to form the fertilized egg, three (rather than two) chromosomes 21 are present. Trisomy 21 Trisomy 21 (also known by the karyotype 47,XX,21 for females and 47,XY,21 for males) is caused by a failure of the 21st chromosome to separate during egg or sperm development (nondisjunction) As a result, a sperm or egg cell is produced with an extra copy of chromosome 21;.
This type of trisomy 21 exclusively occurs sporadically de novo as a result of nondisjunction of homologous chromosomes 21 during gametogenesis to parents or during early embryonic development. Licznerski G, Lindsten J Trisomy 21 in man due to maternal nondisjunction during the first meiotic division. The relative roles of Meiosis I and Meiosis II nondisjunctions in the causation of trisomy 21 have been assessed by analysing the distribution of polymorphic phenotypes of the chromosomes 21 in a group of individuals with Down's syndrome The data suggest that the majority of cases of trisomy 21 are due to meiosis I nondisjunctions.
Trisomy 21 (also known by the karyotype 47,XX,21 for females and 47,XY,21 for males) is caused by a failure of the 21st chromosome to separate during egg or sperm development (nondisjunction) As a result, a sperm or egg cell is produced with an extra copy of chromosome 21;. Allen EG, Freeman SB, Druschel C, et al Maternal age and risk for trisomy 21 assessed by the origin of chromosome nondisjunction a report from the Atlanta and National Down Syndrome Projects Hum Genet 09 Feb;125(1)4152 Ghosh S, Feingold E, Dey SK. What is Down syndrome?.
This cell thus has 24 chromosomes. Since scientists have numbered our chromosomes 1 through 23, the name of the condition – trisomy 21, trisomy 18, or trisomy 13 – indicates the specific chromosome that carries the abnormality For example, in the case of Down syndrome (trisomy 21), there are three copies of chromosome number 21. Down syndrome (trisomy 21) is a genetic disorder It includes certain birth defects, learning problems, and facial features A child with Down syndrome also may have heart defects and problems with vision and hearing A mother’s age at her child’s birth is the only factor linked to the risk of having a baby with Down syndrome.
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) is the most common chromosomal abnormality amongst livebirths, with an incidence of 1/800 It is estimated that 80% of all trisomy 21 pregnancies conceived end as spontaneous abortions or as stillbirths;. Of 61 families of children with trisomy 21, polymorphism of chromosome 21 elucidating the origin of the extra chromosome was found in 42 Nondisjunction was of paternal origin in 8 cases (1904%) and the anomaly occurred with equal frequency during the first and second meiotic divisions Maternal nondisjunction was demonstrated in 34 cases (8095%), in which nondisjunction occurred by far the. Chromosomal aneuploidy is a fundamental characteristic of the human species In this review we summarize the knowledge about the origin and mechanisms of nondisjunction in human trisomy 21 that has.
This cell thus has 24 chromosomes. Somies 21 (Down Syndrome), 18 (Edward's Syndrome) or 13 (Patou Syndrome) increases with the mother's age (Valero et al, 1999) According to Pena (1998), in trisomy 21, the increase in the rate of nondisjunction in meiosis II is higher than for meiosis I if the mother's age is between 35 and 39 years For sexual chromo. Down syndrome is by far the most common and best known chromosomal disorder in humans and the most common cause of intellectual disability It is primarily caused by trisomy of chromosome 21 (see.
Down syndrome (trisomy 21 or DS) is a group of signs, symptoms, and health problems that arise from an error in cell division that results in an extra chromosome 21 This may occur before or shortly after conception and has a widespread effect on the physical and intellectual development of the affected person.

Meiosis And Fertility Associated With Chromosomal Heterozygosity Chapter 7 Shrews Chromosomes And Speciation

Trisomie 21 Alles Uber Das Down Syndrom
Down Syndrome Faq

Pdf Down S Syndrome Etiology And Mechanism Revisited
Docserv Uni Duesseldorf De Servlets Derivateservlet Derivate 3104
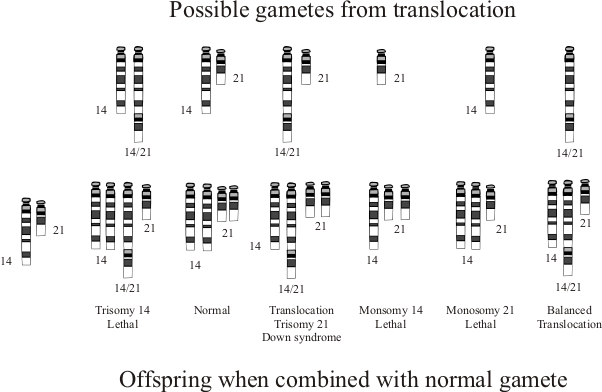
Die Robertson Translokation Als Ursache Des Down Syndroms In Biologie Schulerlexikon Lernhelfer

Down Syndrome Trisomy 21 Pediatrics Msd Manual Professional Edition

Down Syndrome Amboss
Q Tbn And9gct8apsk 1oe5yzhdhhfwvcjqkye3dzpaiga Lnz1mf8pjhxsav Usqp Cau
Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies

Nondisjunction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Molecular Studies Of Parental And Meiotic Stage Of Origin In Autosomal Download Table

Cartoon Illustrating The Different Types Of Secondary Nondisjunction Download Scientific Diagram
Genetics Of Down Syndrome Wikipedia

Formation Of Upd 7 Mat By Trisomic Rescue Snp Array Typing Provides New Insights In Chromosomal Nondisjunction Abstract Europe Pmc
Docserv Uni Duesseldorf De Servlets Derivateservlet Derivate 3104
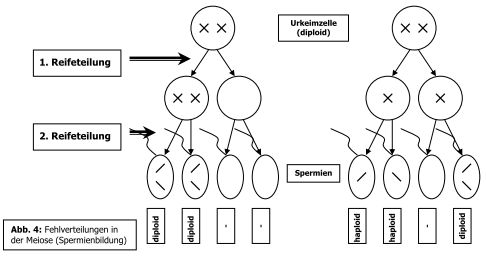
Losungsblatt Down Syndrom Trisomie 21

Pdf Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies

Pdf Trisomy 21 Origin Of Non Disjunction
Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies

S4a0pzbr0kjemm

Chromosome Abnormalities
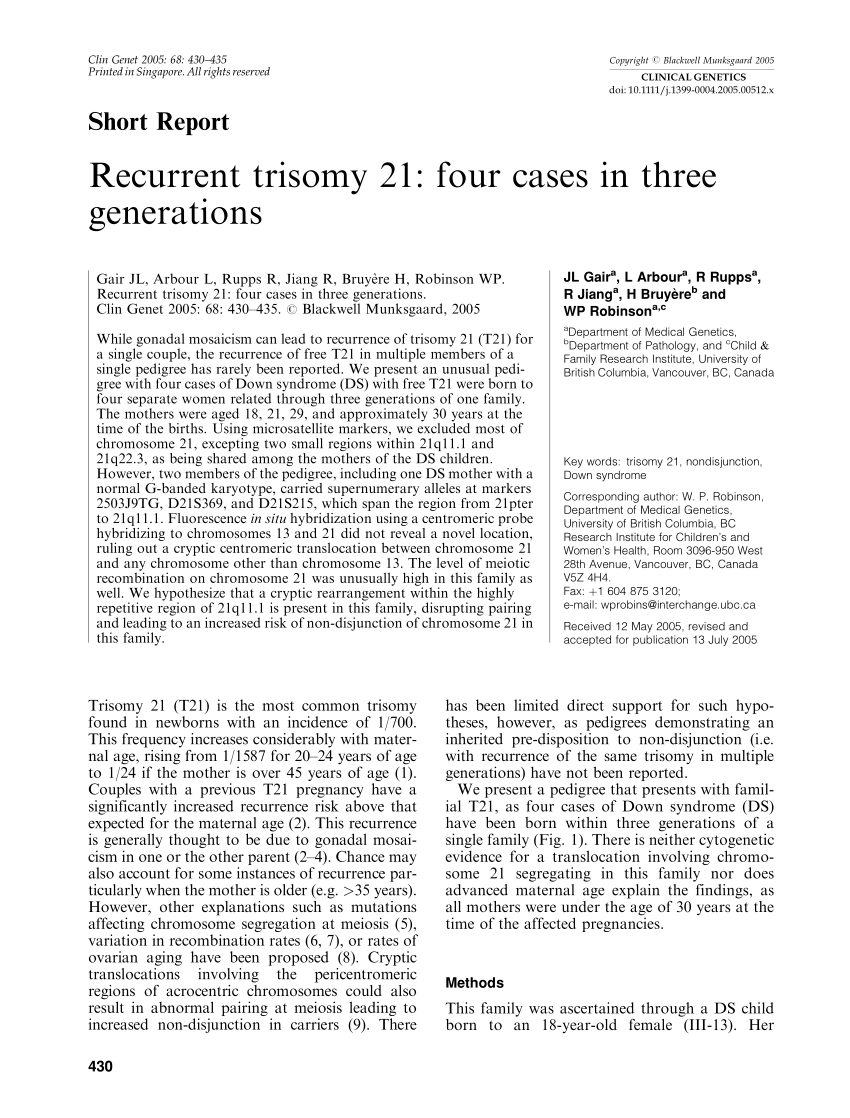
Pdf Recurrent Trisomy 21 Four Cases In Three Generations

Nondisjunction Genetics
Docserv Uni Duesseldorf De Servlets Derivateservlet Derivate 3104

Nondisjunction The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
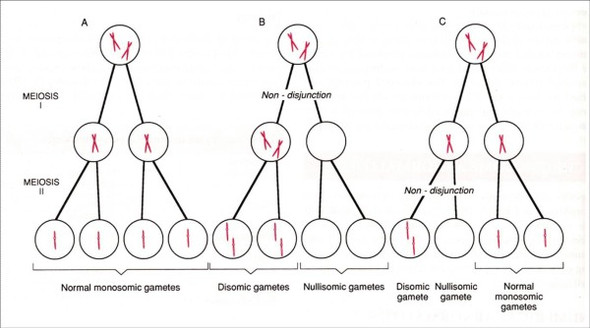
Was Passiert Bei Trisomien Biologie Genetik Trisomie

Parental Origin And Meiotic Error Of Different Autosomal Trisomies Download Table
Http Www U Helmich De Bio Gast Alberts Entwurf2 Pdf
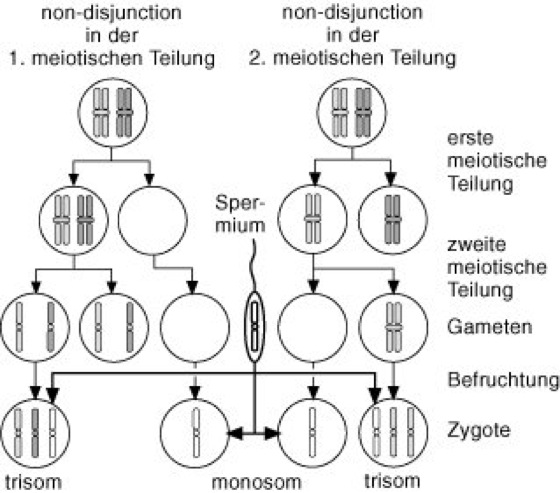
Non Disjunction Lexikon Der Biologie

Trisomy 21 18 And 13 Nondisjunction Genetics Youtube
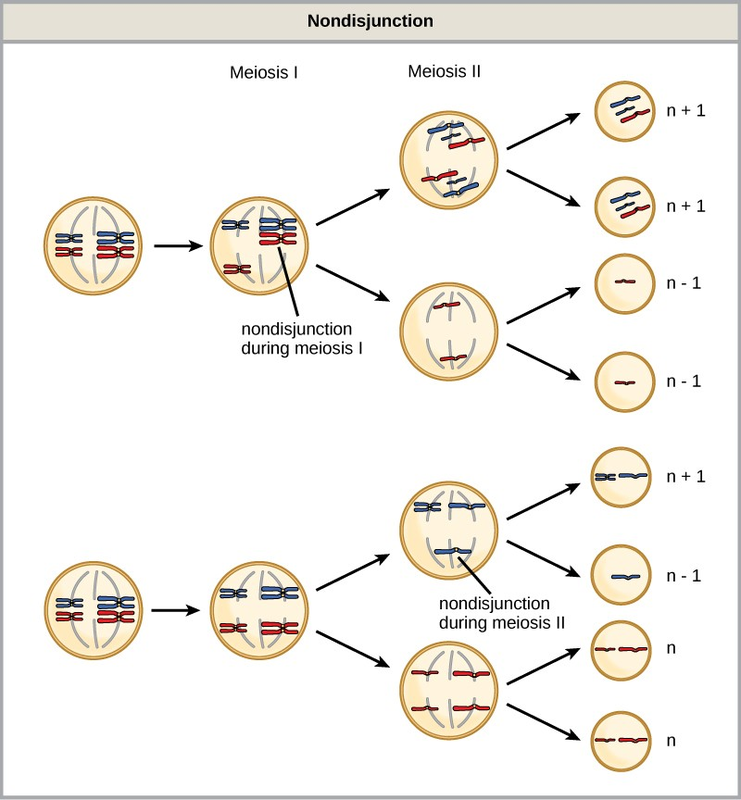
Nondisjunctions Duplications And Deletions Open Textbooks For Hong Kong
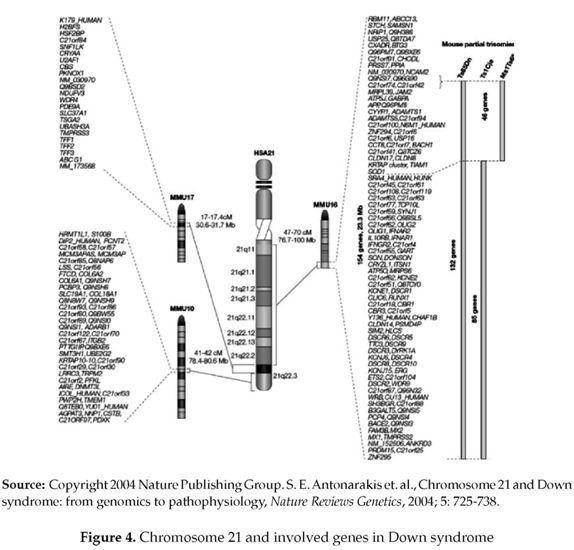
Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies

Cartoon Illustrating The Different Types Of Secondary Nondisjunction Download Scientific Diagram
Http Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 2f978 3 662 1 4 Pdf
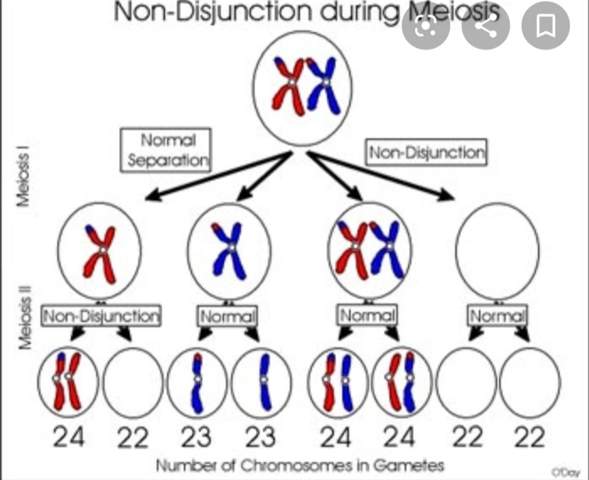
Trisomie 21 Chromosomensatz Biologie Trisomie 21

A Model System For Increased Meiotic Nondisjunction In Older Oocytes Current Biology

Risk Factors For Down Syndrome Birth Understanding The Causes From Genetics And Epidemiology Intechopen

Down Syndrome Trisomy 21 Pediatrics Msd Manual Professional Edition
Ppt Down Syndrome Trisomy 21 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies
Http Www U Helmich De Bio Gast Alberts Entwurf2 Pdf

Down Syndrome Osmosis
Unterrichtsentwurf Fur Die Zweite Lehrprobe Im Fach Biologie Am Studienseminar Oberhausen Pdf Free Download
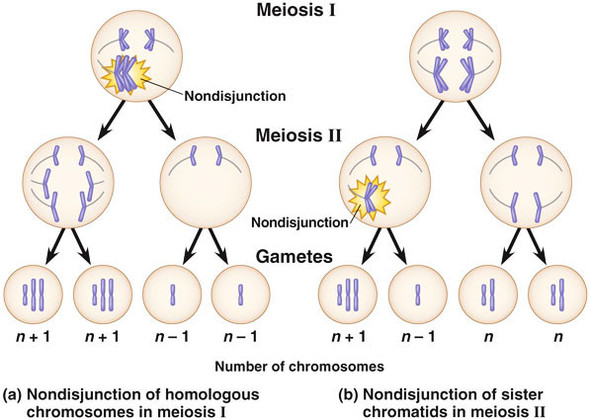
Schaubild Zur Trisomie Biologie Down Syndrom
Unterrichtsentwurf Fur Die Zweite Lehrprobe Im Fach Biologie Am Studienseminar Oberhausen Pdf Free Download
Index Of Bio3400 Locked Media Ch08

Triple X Syndrome Disease Malacards Research Articles Drugs Genes Clinical Trials
Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 2f978 3 662 4 4 Pdf
Trisomie 21 By Joanna Stier On Prezi Next
Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies

Pdf Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies

Chromosomal Diseases Biochemistry Medbullets Step 1
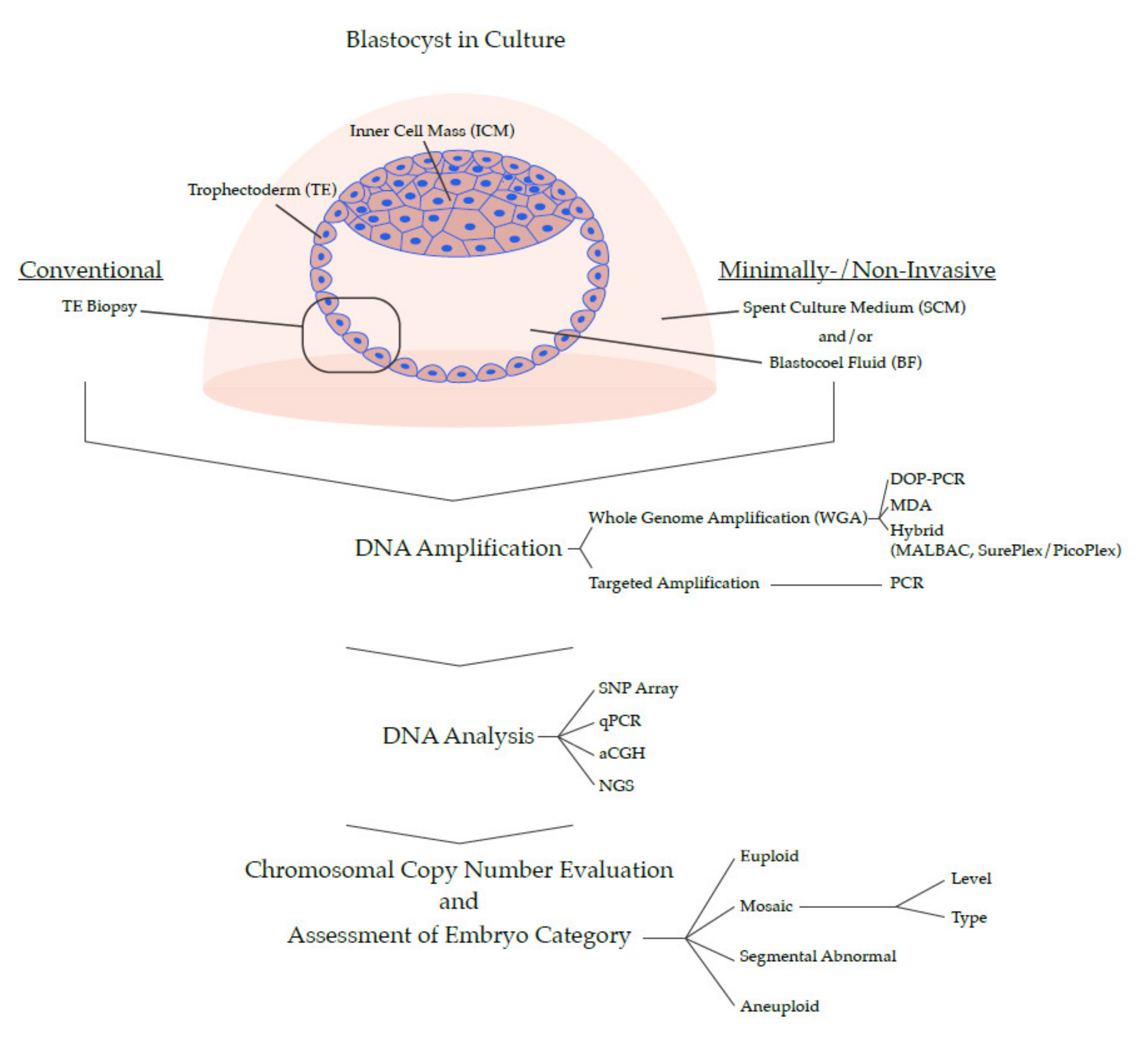
Genes Free Full Text Preimplantation Genetic Testing For Chromosomal Abnormalities Aneuploidy Mosaicism And Structural Rearrangements Html
_und_entwicklung/08.16erbkrankheiten_II/translokation.png)
Freies Biologie Lehrbuch Fur Schuler Und Studenten

Congenital Disorders 3 Chromosomal Disorders

Trisomy 21

Nondisjunction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Non Disjunction Bioninja

Nondisjunction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Q Tbn And9gctrxo2xzfo2c5g0rw40p0hptwmm6besrjr2wufsltkipzaw Kke Usqp Cau
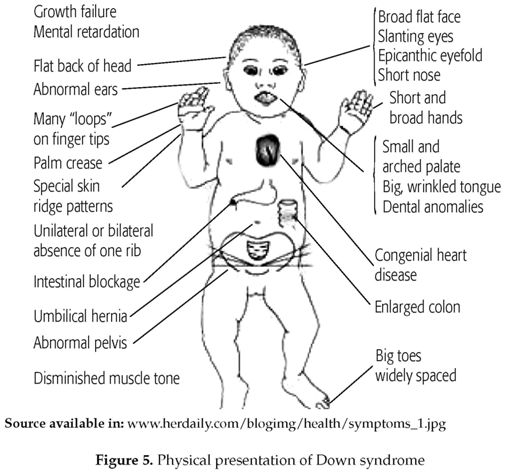
Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies

Trisomie 21 Youtube

Meiosis And Fertility Associated With Chromosomal Heterozygosity Chapter 7 Shrews Chromosomes And Speciation

Unterrichtsentwurf Fur Die Zweite Lehrprobe Im Fach Biologie Am Studienseminar Oberhausen Pdf Free Download
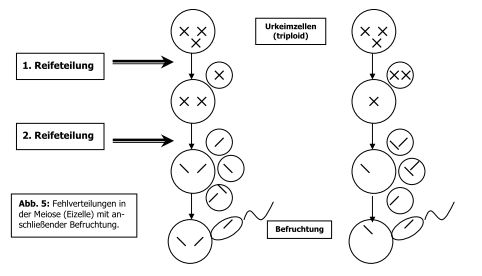
Losungsblatt Down Syndrom Trisomie 21

Chromosomal Basis Of Inherited Disorders Boundless Biology

Trisomie 21 Alles Uber Das Down Syndrom
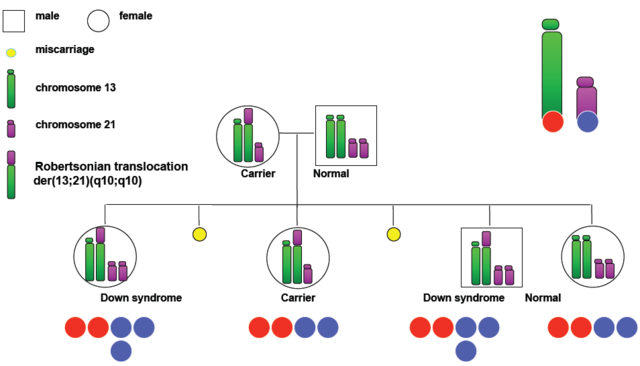
Trisomie 21 Alles Uber Das Down Syndrom
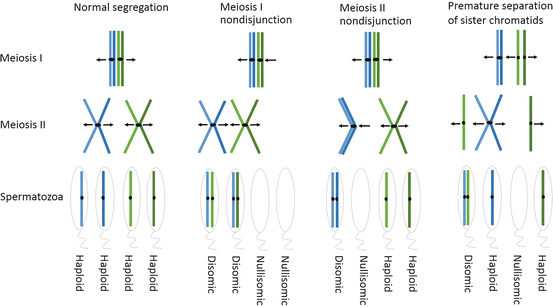
Meiotic Nondisjunction Insights Into The Origin And Significance Of Aneuploidy In Human Spermatozoa Basicmedical Key
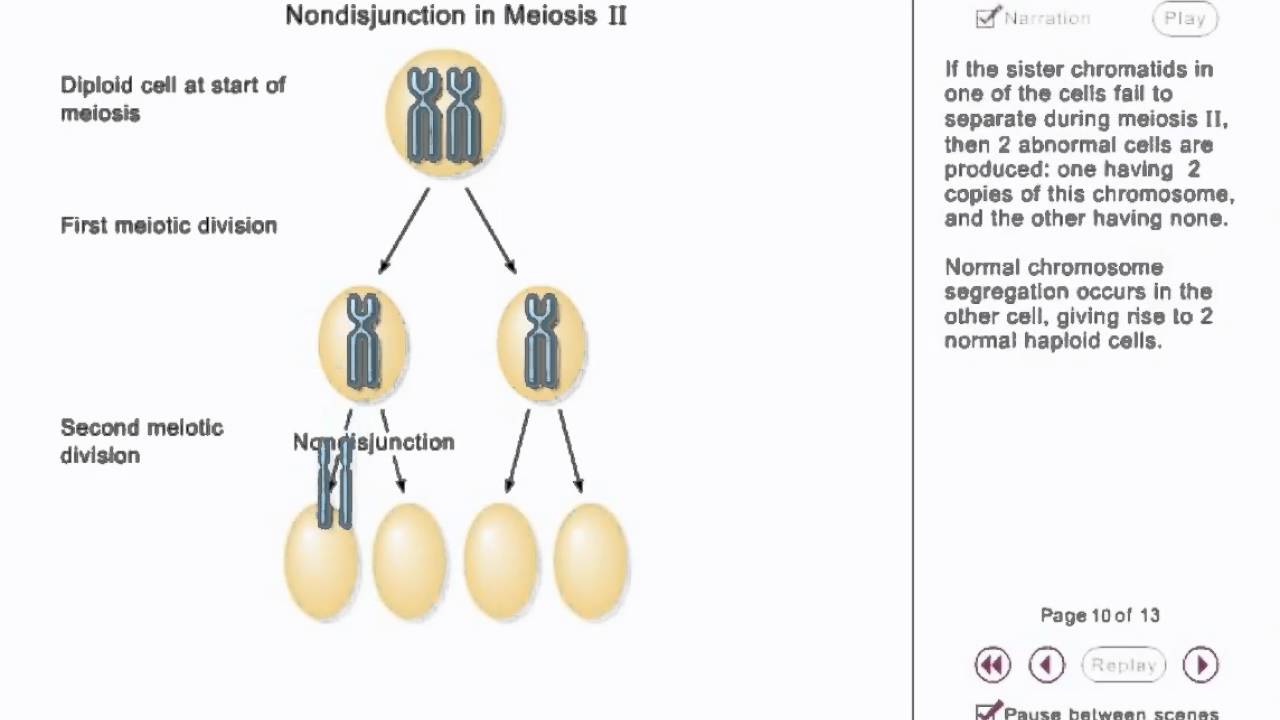
Chromosome Nondisjunction Animation Youtube

Nondisjunction The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Pdf Origin And Mechanisms Of Non Disjunction In Human Autosomal Trisomies Semantic Scholar

Association Between Telomere Length And Chromosome 21 Nondisjunction In The Oocyte Semantic Scholar
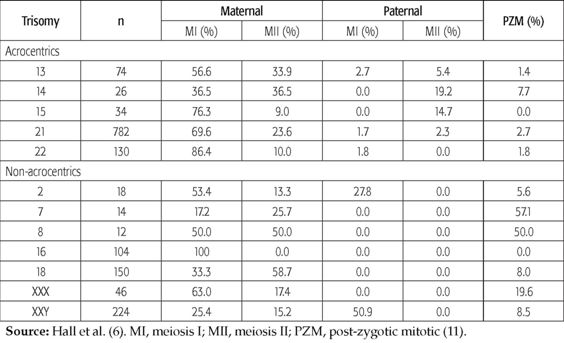
Nondisjunction And Chromosomal Anomalies

Deviating Chromosome Number Or Structure

Nondisjunction Wikipedia
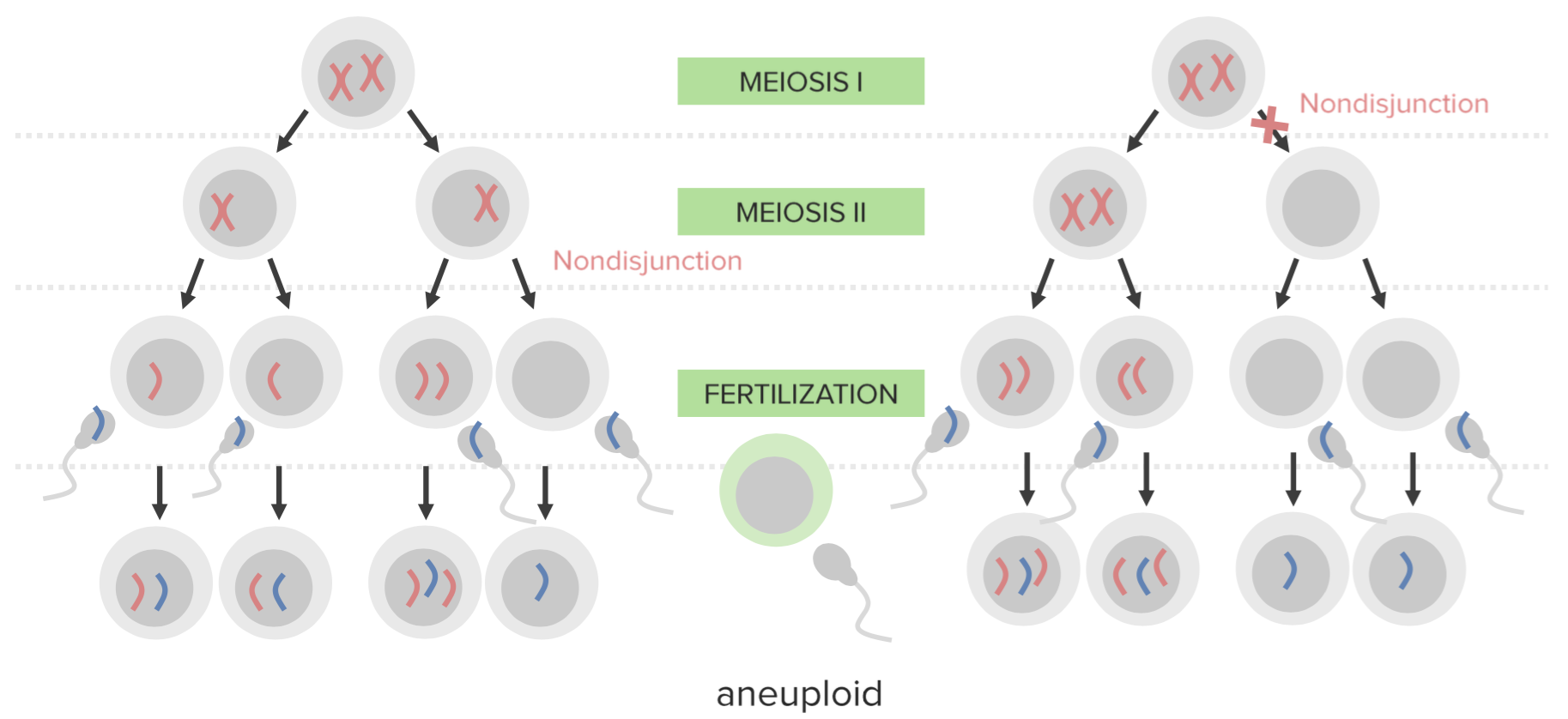
Nondisjunction Definition And Examples Online Medical Magazine

Schematic Representation Of Mechanisms Leading To Chromosome Mosaicism Download Scientific Diagram

13 2 Chromosomal Basis Of Inherited Disorders Texas Gateway
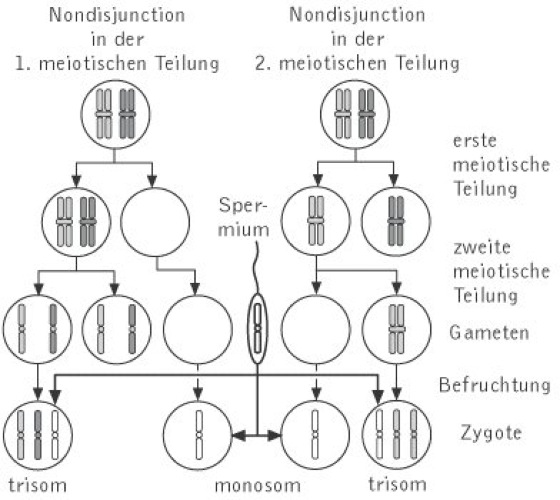
Non Disjunction Kompaktlexikon Der Biologie
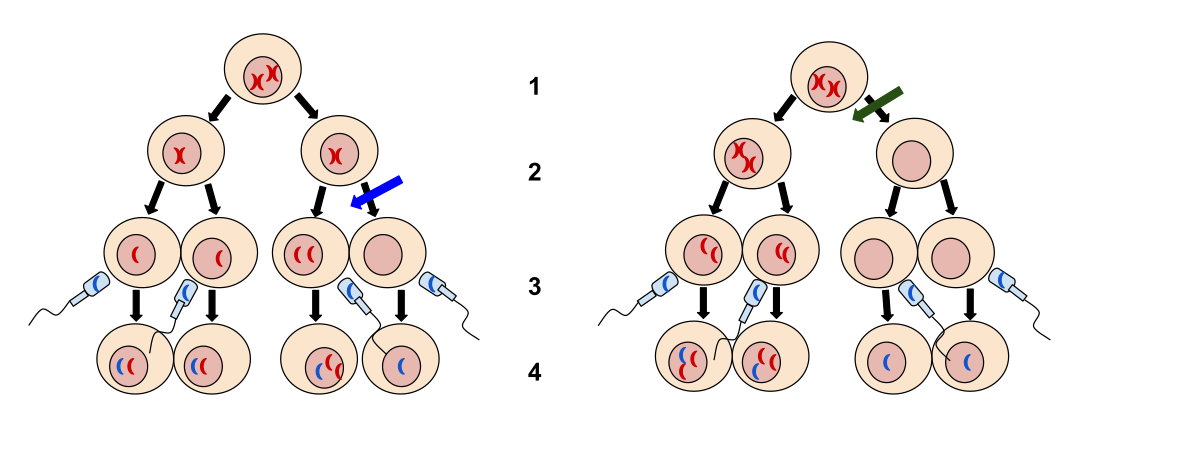
Nondisjunction Wikipedia
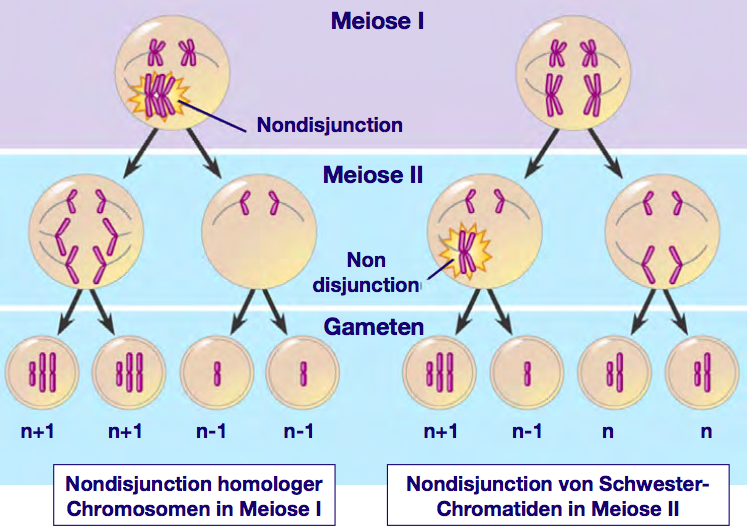
Chromosomenaberrationen Anderung Der Chromosomenzahl Genetik Repetico
Docserv Uni Duesseldorf De Servlets Derivateservlet Derivate 3104
Q Tbn And9gcqm Iv9eq Yd Pj5mpxehtqpmue0ttepifpzfqtkwms6nhlok8v Usqp Cau

Nondisjunction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Nondisjunction An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Http Europepmc Org Articles Pmc Pdf Ajhg 0017 Pdf

Non Disjunction Bioninja
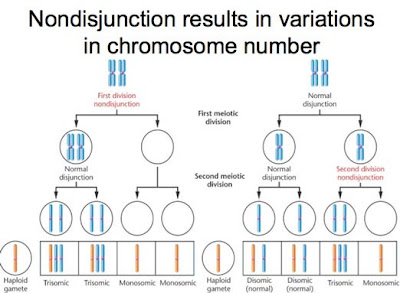
Why Does Nondisjunction Cause Mutation Socratic
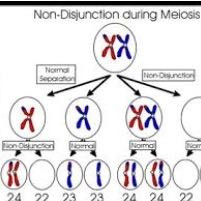
Ist Bei Trisomie 21 Eine Non Disjunction Bei Der Meiose 1 Oder Bei Der Meiose 2 Wahrscheinlicher Biologie Down Syndrom Trisomie 21

Meiosis And Fertility Associated With Chromosomal Heterozygosity Chapter 7 Shrews Chromosomes And Speciation

Origin Of Trisomy 21 And Their Frequency In Indian Cohort Download Table
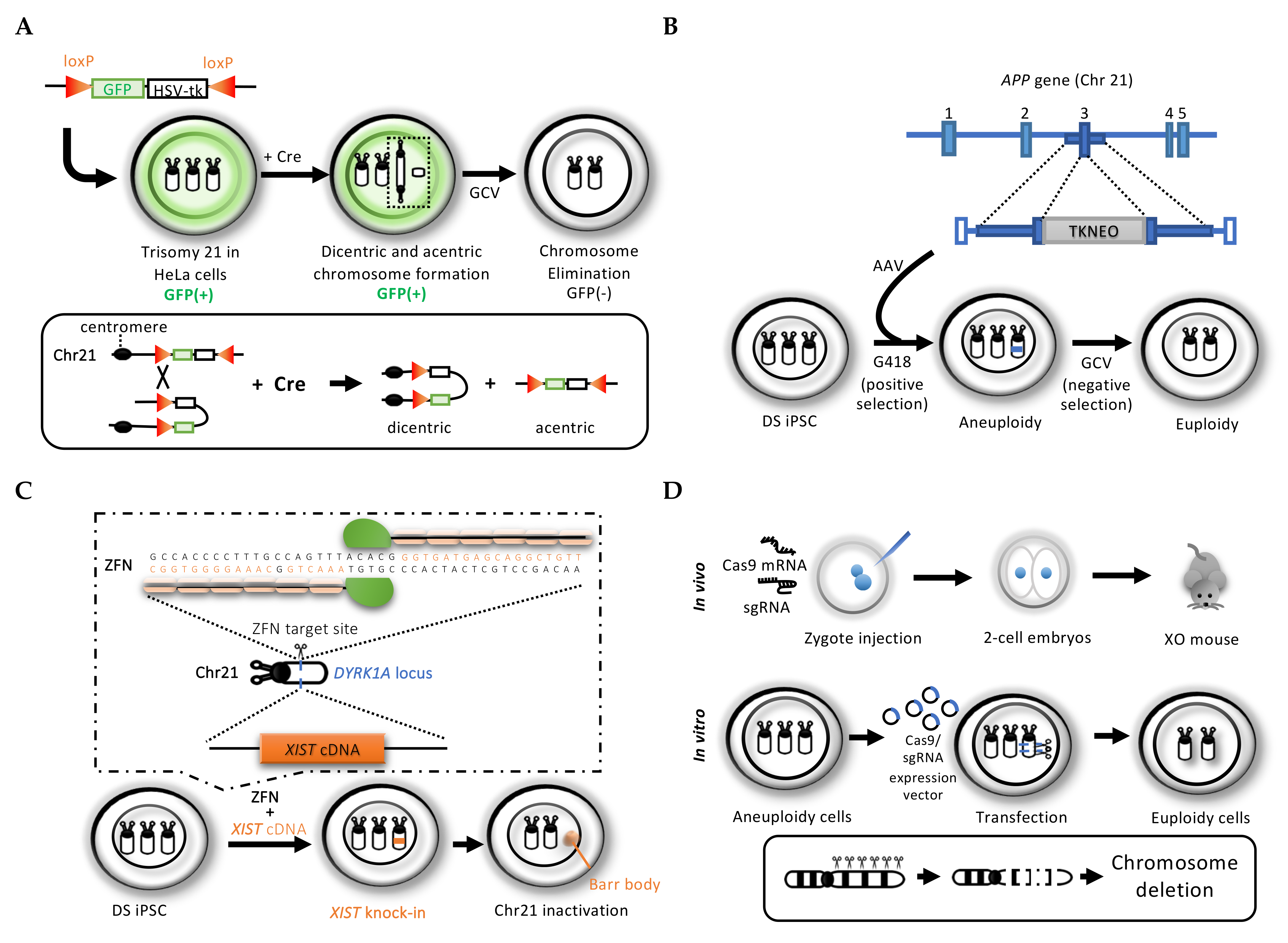
Cells Free Full Text Applications Of Genome Editing Technology In Research On Chromosome Aneuploidy Disorders Html
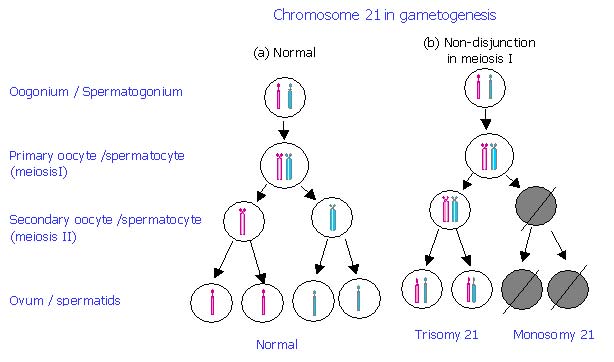
Nondisjunction In Meiosis Nondisjunction Disorders Bioexplorer

Parodontitis Bei Down Syndrom Trisomie 21 Eine Literaturubersicht Erganzt Durch Eine Querschnittsuntersuchung Pdf Free Download

Trisomie 21 Youtube
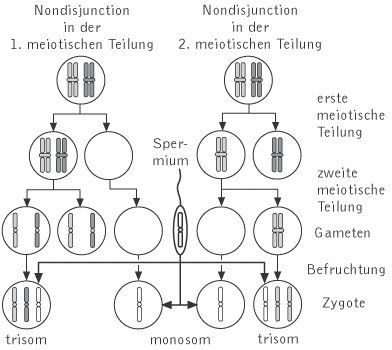
Non Disjunction Kompaktlexikon Der Biologie



