Absolute Encoder Types

Designing An Emc Compliant Interface To Motor Position Encoders Part 1 Industrial Technical Articles Ti E2e Support Forums

What Is The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders Realpars

S3d5sbrayim72m

What Is The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders Realpars

What Is Rotary Encoder Construction Working Types

What Is An Absolute Encoder Zettlex Inductive Encoders
Types of Rotary Encoders 1 Mechanical Absolute Rotary Encoders An absolute rotary encoder gauges an absolute angle of the encoded shaft by having an interesting code for each shaft position With that, each position of the estimation range/point is being distinguished by a specific code on a plate.

Absolute encoder types. A rotary encoder, also called a shaft encoder, is an electromechanical device that converts the angular position or motion of a shaft or axle to an analog or digital output signals There are two main types of rotary encoder absolute and incremental. Our Bulletin 845GM SingleTurn is a NEMA Type 4 and 13, singleturn absolute encoder that digitizes shaft position for reliable readouts You can use this encoder under a wide range of harsh conditions The 845GM provides high resolution in a compact size housing for applications where positioning accuracy is critical but space is limited. Absolute rotary encoders maintain positional values on the loss of power The synchronisation of new positional values resume on power restoration, so unlike incremental encoders, there is no need to reset the encoder or other electrical devices on restart The most popular type of encoder is an optical rotary encoder.
Both linear and rotary encoders are available as either absolute or incremental encoders, which describes the desired signal output for the encoder With an absolute encoder, the output signal generated by the device results in a unique set of digital bits that correspond to a specific position of the object being measured. Absolute encoders typically output either a digital data stream, such as serial synchronous interface ( SSI) or an analogue signal such as 010V or 4mA Incremental encoders typically output pulses which are often described as A/B pulse or ‘A quad B’ encoders. Absolute encoder This type of encoder can provide the specific location, the absolute encoders can be singleturn or multiturn The singleturn encoders are suitable for short travel applications while the multiturn encoders are suitable for long position applications The components of an absolute encoder are almost the same as in the.
Encoder Products Company (EPC) is a leading manufacturer of premium rotary incremental and absolute encoders used for motion feedback Our encoders are available worldwide to OEMs, MROs, End Users, Service/Repair Organizations and others through a qualified network of electrical, motion control, and industrial distributors. Absolute Encoders Reference EtherCAT® EtherCAT® is a protocol optimized for process data, using standard IEEE 8023 Ethernet Frames Each slave PROFINET® PROFINET® is widely used by major industrial equipment manufacturers PROFINET RT can be used in PLCtype CANOpen® CANopen® is a. Our Bulletin 845GM SingleTurn is a NEMA Type 4 and 13, singleturn absolute encoder that digitizes shaft position for reliable readouts You can use this encoder under a wide range of harsh conditions The 845GM provides high resolution in a compact size housing for applications where positioning accuracy is critical but space is limited.
Absolute Encoder Product Finder Incremental Rotary Encoders Incremental encoders generate an output signal each time the shaft rotates a certain amount (The number of signals per turn defines the resolution of the device) Each time the encoder is powered on it begins counting from zero, regardless of where the shaft is. Absolute Encoder Product Finder Incremental Rotary Encoders Incremental encoders generate an output signal each time the shaft rotates a certain amount (The number of signals per turn defines the resolution of the device) Each time the encoder is powered on it begins counting from zero, regardless of where the shaft is. Table 6 Absolute Encoder (Product Type) Market Share Breakdown of Worldwide Sales by Region/Country 12 VS VS 27 Table 7 Incremental Encoder (Product Type) Potential Growth.
Absolute encoders are available as singleturn or multiturn types, with singleturn versions providing position data over one full revolution of 360°, which repeats for every revolution of the shaft The multiturn type has a turns counter that enables the encoder to output not only the shaft position but also the number of revolutions. All variations of Absolute Encoders are available ie absolute position, shaft, optical, multi turn, linear, rotary, hollow shaft encoders Enquire Now Why choose Encoders UK for Absolute Encoders. Types of Rotary Encoders Rotary encoders are classified according to the type of output they produce There are two main types of rotary encoders Incremental encoders;.
An encoder that detects how far from the home position is called an absolute angle detection type When comparing to a map, the absolute angle detection type tells you that there is a convenience store at ABC town, Chiyodaku, Tokyo The absolute angle detection type encoder outputs the current absolute angle in a digital serial code or an analog voltage in response to instructions from the microcomputer. Absolute encoders typically output either a digital data stream, such as serial synchronous interface ( SSI) or an analogue signal such as 010V or 4mA Incremental encoders typically output pulses which are often described as A/B pulse or ‘A quad B’ encoders. Absolute optical encoders provide and record the unique values of each shaft position This is especially important in the event of a power failure after which time machine operation will continue from the point where it stopped Gray and binary codes are the most common types of numerical encoding used in absolute optical encoders.
Absolute Encoder Type Electric Actuators LEm Series CATESA 0 5 10 15 30 25 0 0 400 600 800 1000 10 Work load W kg Speed V mm/s Lead 6 LEFS25EB Lead 12 LEFS25EA Lead LEFS25EH 0 100 0 300 400 500 600 Work load W kg Speed V mm/s 0 5 10 15 Lead 6 LEFS25EB. It’s common to see both in many industrial applications However, since each type of encoder produces different types of output, they are used in different. Encoders are vital to motion systems Data suggests the encoder market will experience a significant spike in growth by 22 The market is currently dominated by two types of encoders Absolute encoders and incremental devices.
Two of the most common encoder types — absolute and incremental — output different information Take a look at the quick oneminute video below from one of our engineers to get a better understanding of the differences An incremental encoder is an encoder that outputs either a square or a sine/cosine wave The number of periods can be. There are two types of absolute encoders singleturn and multiturn encoders Singleturn encoders measure displacement in one turn or across 360 deg from a starting position The output is. There are many different types of encoders but they basically fall into two main sensing techniques Those being – Linear – Rotary Within those categories, there are differing encoder measurement types such as – Absolute – Incremental There are also various electromechanical technologies such as – Magnetic – Optical – Inductive.
Absolute rotary encoders measure actual position by generating unique digital codes or bits (instead of pulses) that represent the encoder's actual position Single turn absolute encoders output codes that are repeated every full revolution and do not output data to indicate how many revolutions have been made. Absolute encoder This type of encoder can provide the specific location, the absolute encoders can be singleturn or multiturn The singleturn encoders are suitable for short travel applications while the multiturn encoders are suitable for long position applications The components of an absolute encoder are almost the same as in the. Encoders come in two types absolute and incremental encoders Absolute encoders give an absolute position because of the unique code pattern assigned to each angle increment, The code pattern is used to reference a specific position to a control unit This encoder type is generally used in transport logistics, robotics, and other applications where controlling and monitoring the exact position is important.
A rotary encoder is a type of sensor used to detect the angular position or movement of a rotating shaft The goal of the sensor is to convert the rotational motion of the shaft into analog or digital signals, which are then transmitted to the central PLC systemThis information is then processed through the PLC’s algorithm to come up with a suitable response. Digital optical encoders have both linear and rotary configurations, but the most common type is rotary (both incremental optical encoders and absolute optical encoders are rotary configurations) Most rotary encoders are made of glass or plastic with photographically etched tracks similar to those on a compact disc. An absolute encoder has multiple code rings with various binary weightings which provide a data word representing the absolute position of the encoder within one revolution This type of encoder is often referred to as a parallel absolute encoder A multiturn absolute rotary encoder includes additional code wheels and gears.
An absolute encoder has a unique code for each shaft position which represents the absolute position of the encoder, while an incremental encoder generates an output signal each time the shaft rotates a certain angle and the number of generated pulses is proportional to the angular position of the shaft. Table 4 Absolute Encoder (Product Type) World Market by Region/Country in US$ Thousand to 27 Table 5 Absolute Encoder (Product Type) Historic Market Analysis by Region/Country in US$ Thousand 12 to 19 Table 6 Absolute Encoder (Product Type) Market Share Breakdown of Worldwide Sales by Region/Country 12 VS VS 27. An absolute encoder’s resolution is defined as the number of bits in its output word This output can be in straight binary or in gray code, which produces only a singlebit change at each step to reduce errors The difference between incremental and absolute encoders is analogous to the difference between a stop watch and a clock.
Insulated shaft types providing excellent cost performance;. Absolute encoders use internal sensing to measure the angular position directly and maintain this measurement ability even if the power to it is turned off Absolute Encoder MultiTurn In addition to knowing the shaft position, multiturn absolute encoders can also determine how many turns an encoder has made in one direction or the other. Absolute optical encoders employ signalprocessing components similar to those of the quadrature optical encoder, but their outputs produce one parallel binary word per increment of revolution.
Dunkermotoren manufactures & supplies Absolute encoders, Magnetic encoders, Digital encoders and Tacho generators We also offers servo components For more encoder details call today!. The HD25A optical encoder is a 12bit absolute rotary position sensor, which reports a shaft angle within a single 360 degree rotation of a shaft Unlike incremental, sometimes called relative style encoders, the HD25A provides true (absolute) shaft position, eliminating the need for a home or zero cycle after a supply voltage power cycle. Absolute encoders offer a single code for each position and are divided into two groups singleturn encoders and multiturn absolute encoders Their size is small, which allows for a simpler integration Absolute encoders are used in direct current brushless electric motors, in specific industries such as healthcare machinery.
Both linear and rotary encoders can be differentiated into two main types absolute and incremental based on how they work The main difference is that an absolute encoder will detect the absolute position of the encoder, while incremental encoders will only detect changes in movements Incremental Encoder. Singleturn encoders provide positioning data over one full revolution, 360°, with the output repeating for every revolution of the shaft Multiturn encoders also provide positioning data over a single turn, but have an additional “turns” counter that measures the number of revolutions. The AMT21 series is the fastest encoder in the AMT absolute encoder line This encoder offers high resolution position at 12 or 14 bits, comes with radial or axial connector orientations, and has a very simple command protocol.
Types of Rotary Encoders Rotary encoders are classified according to the type of output they produce There are two main types of rotary encoders Incremental encoders;. Encoders Alps Alpine has expanded the scope of applications for its encoders from audio equipment to automotive products and household appliances, catering to customer needs with a broad lineup that includes longlife metal shaft types with minimal shaft play;. Encoders can be either absolute or incremental Absolute encoders have a unique code for each shaft position Or in other words, every position of an absolute encoder is distinctive The absolute encoder interprets a system of coded tracks to create position information where no two positions are identical.
What are rotary encoders?. Ring types with extensive inner and outer diameter variations;. Absolute encoders also have their own types of encoders Single turn absolute encoders provide information for any increment within one shaft rotation Multiturn absolute encoders retain absolute position data over the course of multiple shaft rotations If exact position is needed, absolute encoders would be the best type of encoder to provide that.
Linear encoder feedback Absolute or incremental When selecting a linear encoder, the first thing to consider is what type of feedback is needed for the application—absolute or incremental Absolute encoders assign a unique digital value to each position, which allows them to maintain precise position information, even when power is lost. Products »WEB Catalog » Electric Actuators/Cylinders » Batteryless Absolute Encoder Type ・Restart from the last stop position is possible ・Easy operation restart after recovery of the power supply The position information is held by the encoder even when the power supply is turned off. The Most Common Types of Encoders Linear Encoders These measure straightline motion Sensor heads that attach to the moving piece of machinery run along Rotary Encoders Rotary encoders measure rotational movement They typically surround a rotating shaft, sensing and Angle Encoders Similar.
ABSOLUTE ENCODERS The other type of encoders are absolute encoders As the name suggests, this is the type of encoder that always knows where it is In other words, in opposite to relative encoders, you don’t need to "reinitialize" them They have a certain way to recognize that they are in a certain orientation. Absolute encoders use internal sensing to measure the angular position directly and maintain this measurement ability even if the power to it is turned off Absolute Encoder MultiTurn In addition to knowing the shaft position, multiturn absolute encoders can also determine how many turns an encoder has made in one direction or the other. Absolute encoder Absolute rotary encoder Construction Digital absolute encoders produce a unique digital code for each distinct angle of the shaft They come in two basic types optical and mechanical Mechanical absolute encoders.
When you need to measure the speed, direction of motion or position of a rotating shaft, you will likely require a rotary encoder And when it comes time to choose one, there are two main types to consider the incremental encoder and the absolute encoder Making the right choice is important, which is why we have put together this short guide to absolute encoders, to help you understand what. Products »WEB Catalog » Electric Actuators/Cylinders » Batteryless Absolute Encoder Type ・Restart from the last stop position is possible ・Easy operation restart after recovery of the power supply The position information is held by the encoder even when the power supply is turned off. Absolute encoders generate information about position, angle, and rotation counts in typespecific angle steps For this, a unique code pattern is assigned to each angle increment The number of code patterns available per revolution determines the resolution Each code pattern forms a unique reference, and is therefore an absolute position.
Absolute encoders are of two types Single turn absolute encoder provides information for any increment within one shaft rotation Multi turn absolute encoders are provides information for multiple shaft rotation as many as half billion shaft rotation Thus exact shaft rotation is known even after power interruption. The main drawback for this type of encoder is that they will lose position information if power is lost or cycled As their name implies, absolute encoders report absolute position—even if power is cycled “Every sector of the internal disk in an absolute encoder has a unique pattern,” said Donowitz. It’s common to see both in many industrial applications However, since each type of encoder produces different types of output, they are used in different.
Absolute encoders are available as singleturn or multiturn types, with singleturn versions providing position data over one full revolution of 360°, which repeats for every revolution of the shaft The multiturn type has a turns counter that enables the encoder to output not only the shaft position but also the number of revolutions. We have two types of absolute devices, namely Singleturn and multiturn devices The Singleturn device is responsible for calculating displacement in a single turn from a starting position. The rotary encoder is a proven and popular solution for measuring the speed, direction of motion or position of a rotating shaft Several different types are available, the main two being the absolute encoder and the incremental encoder.
Absolute encoders are available with parallel, serial or fieldbus outputs to transmit shaft position data Absolute encoders with parallel outputs require an output for each bit of information For example, an absolute encoder with a 12bit parallel output would require twelve separate outputs to transmit the data. These are increasingly used for a multitude of jobs in consumer and industrial equipment Rotary encoders, or shaft encoders, can in principle, be absolute or incremental An absolute encoder provides position information when the power is lost, whereas an incremental encoder is used where velocity and direction information is required Both can be used with angular as well as linear displacements, but they operate differently. Absolute encoder This type of encoder can provide the specific location, the absolute encoders can be singleturn or multiturn The singleturn encoders are suitable for short travel applications while the multiturn encoders are suitable for long position applications The components of an absolute encoder are almost the same as in the.
Absolute encoders are either singleturn or multi turn encoders Single turn absolute encoders can verify position within a single turn of the encoder shaft This makes them useful for short travel situations In contrast, multipleturn absolute encoders are better for more complex or longer positioning situations.

Intech Chennai

Understanding Resolution In Optical And Magnetic Encoders Electronic Design

Basics Of Rotary Encoders Overview And New Technologies Machine Design
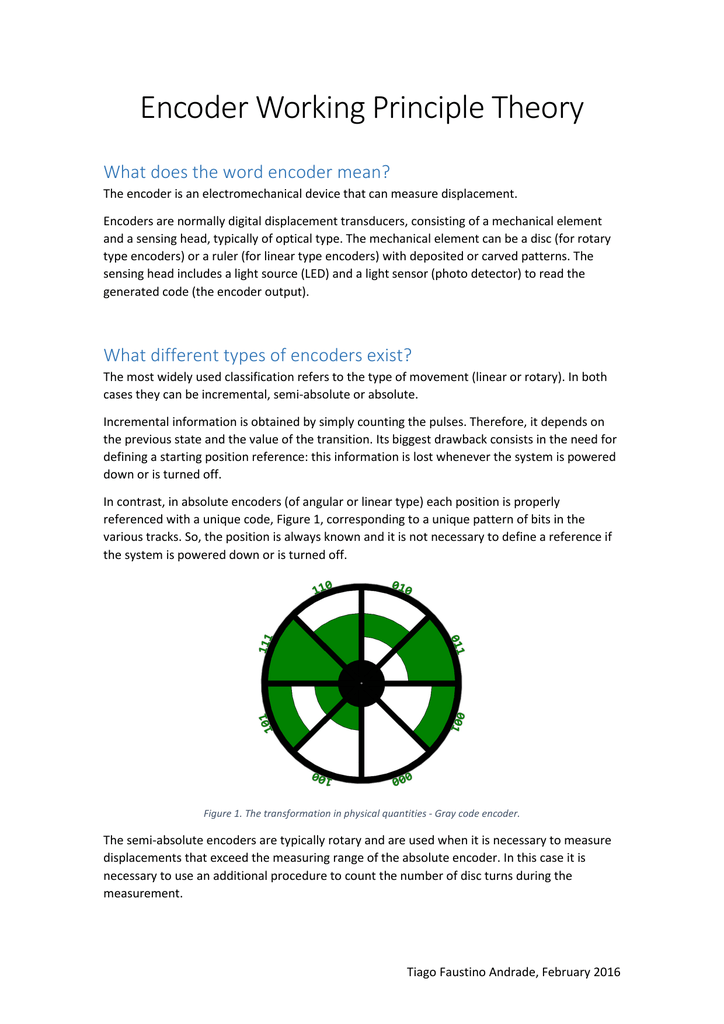
Encoder Working Principle Theory

Encoder Working Principle Encoder Animation Instrumentation Tools

Absolute Vs Incremental Encoder What Is The Difference Advantages And Disadvantages
1
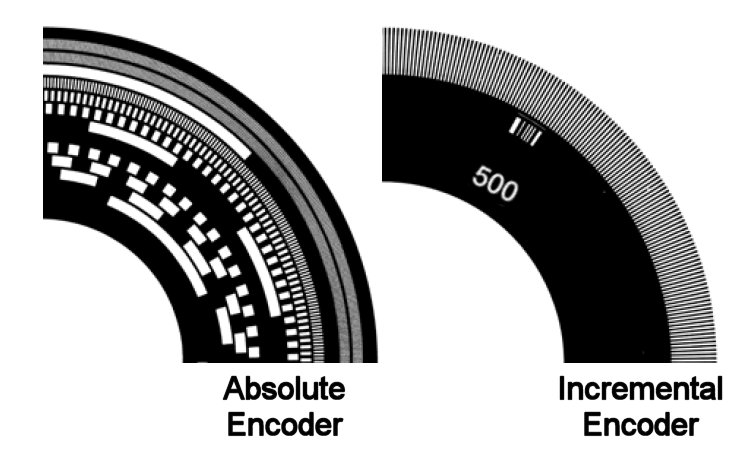
Basics Of Rotary Encoders Precision Electronic Services Inc

Efrain Teran Carol Young Brian O Saben Ppt Download

Basics Of Rotary Encoders Overview And New Technologies Machine Design
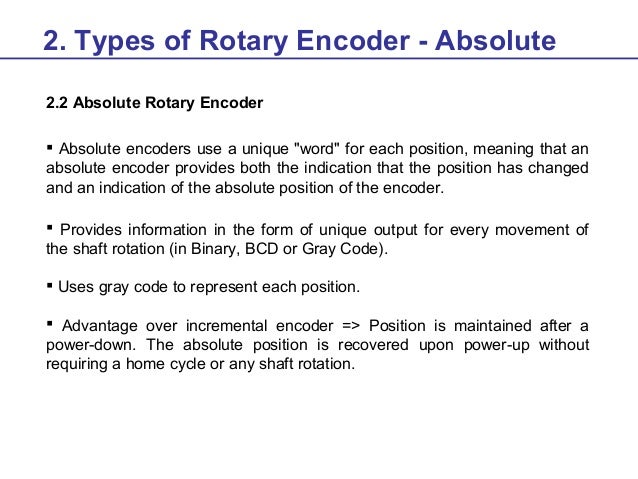
Rotary Encoder Training Material

Encoders Optical And Magnetic Incremental And Rotary
1
Support Industry Siemens Com Cs Attachments Geberparametrierung V1d0 En Pdf

Absolute Position Encoder With Non Contact Magnetic Sensor
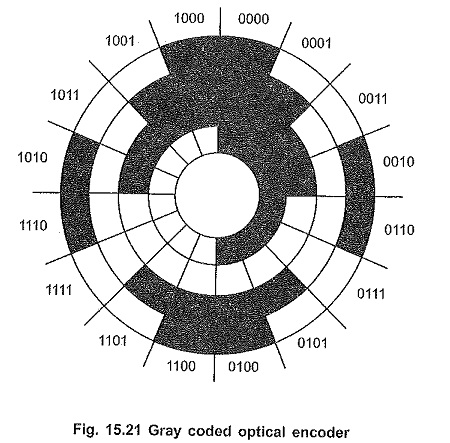
Optical Encoders Types Of Optical Motor Shaft Encoders

What Is The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders Realpars
When Is An Absolute Encoder Right For Your Design Cui Devices
.jpg)
Absolute Vs Incremental Encoder What Is The Difference Advantages And Disadvantages
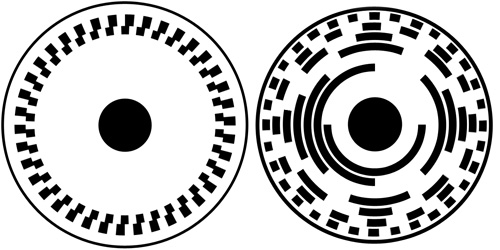
Encoder Primer Phidgets Support
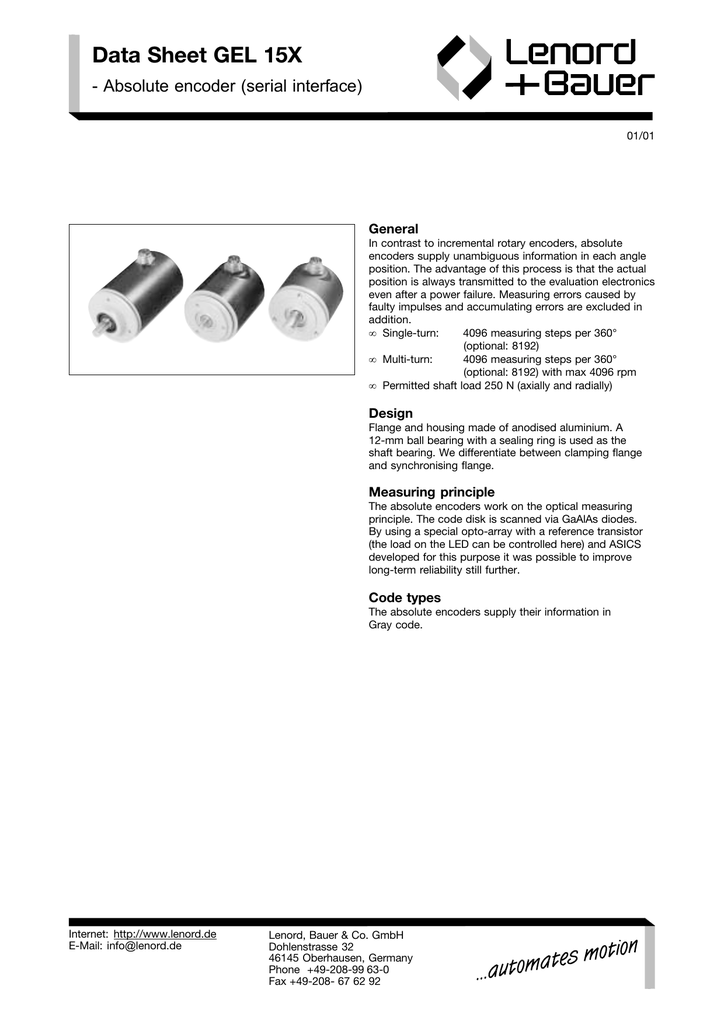
Data Sheet Gel 15x Absolute Encoder Serial Interface General Manualzz

Encoders Basic Training Ppt Download
When Is An Absolute Encoder Right For Your Design Cui Devices

What Is An Absolute Encoder When To Use It Quickmechy

Linear Encoder Types And Selection Motion Control Tips

A Look Into Rotary Encoder Types Absolute And Incremental Technical Articles
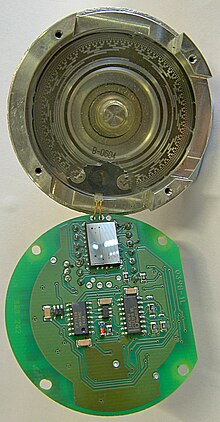
Rotary Encoder Wikipedia
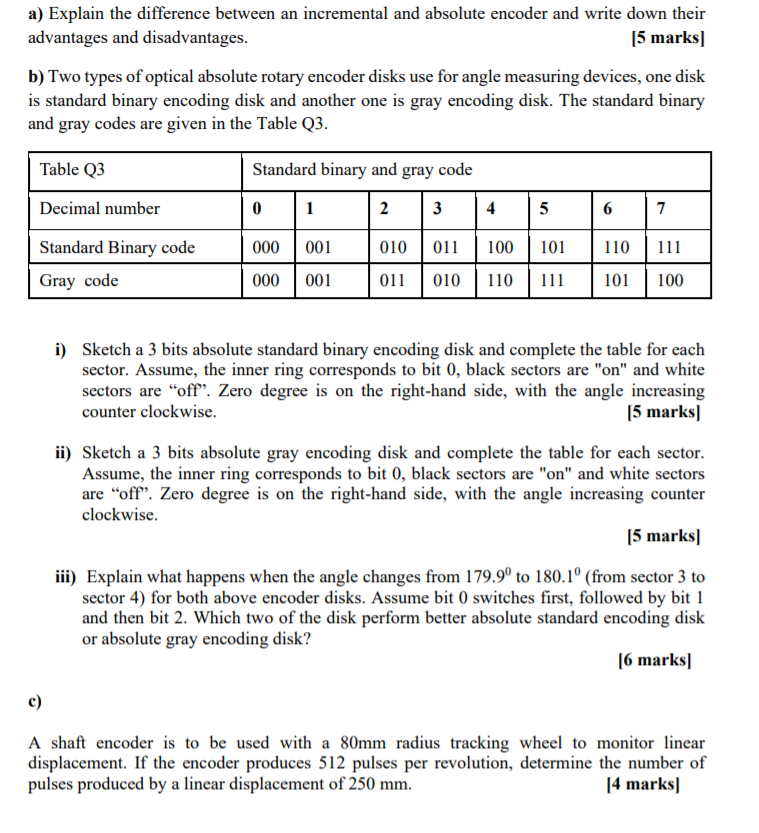
Solved A Explain The Difference Between An Incremental A Chegg Com

Incremental Encoders How They Work And What Are Their Benefits

Absolute Or Incremental Encoders The Differences Explained Sick Usa Blog
%20(1).jpg)
Absolute Vs Incremental Encoder What Is The Difference Advantages And Disadvantages
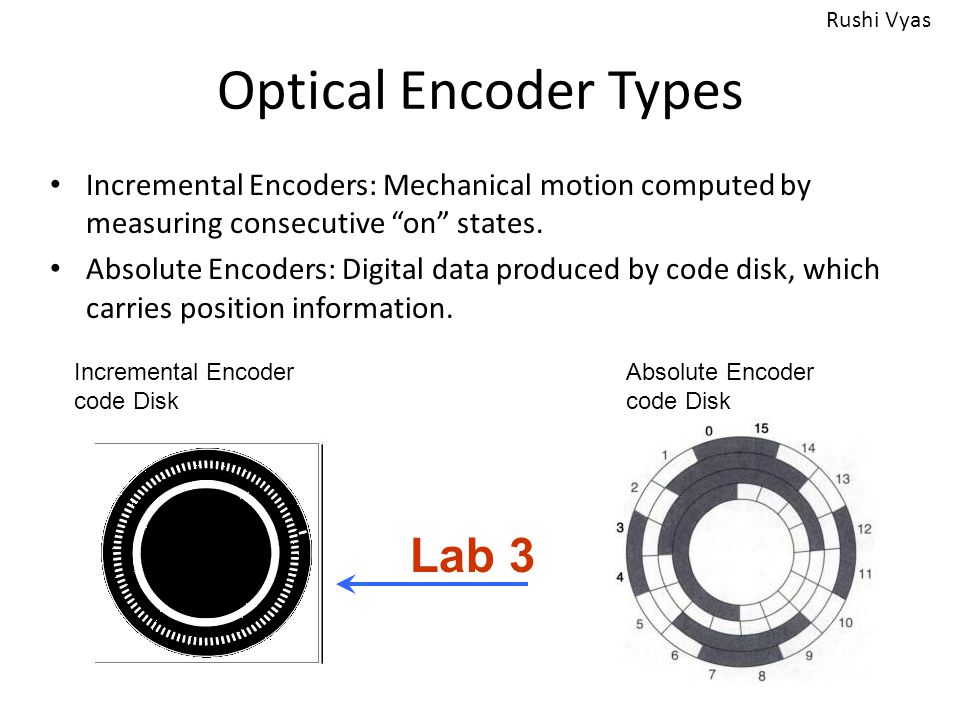
Optical Encoders Laser Interferometer Lvdt Ppt Video Online Download

Incremental Encoder And Absolute Encoder

Incremental Absolute Encoders What S The Best Solution For Your Application Pdf Free Download

Rotary Encoders Gurley Precision Instruments

How Encoder Resolution Is Determined

Absolute Encoder Gel 15x Preferred Types Parallel Interface General Manualzz

Faq What Is The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders
What Is The Purpose Of Encoder Types Of Encoder Urdu Hindi Youtube
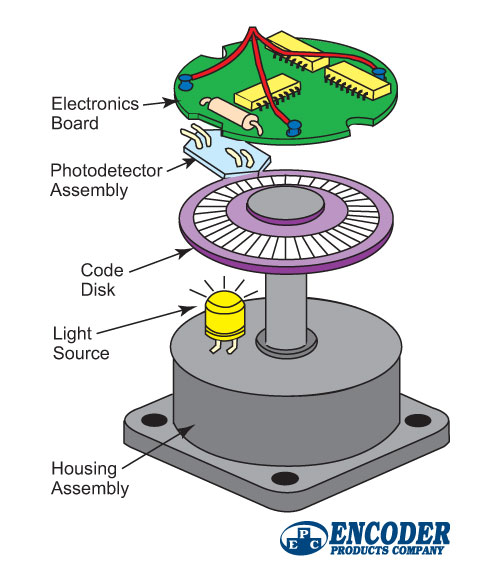
What Is An Encoder Roboticstomorrow

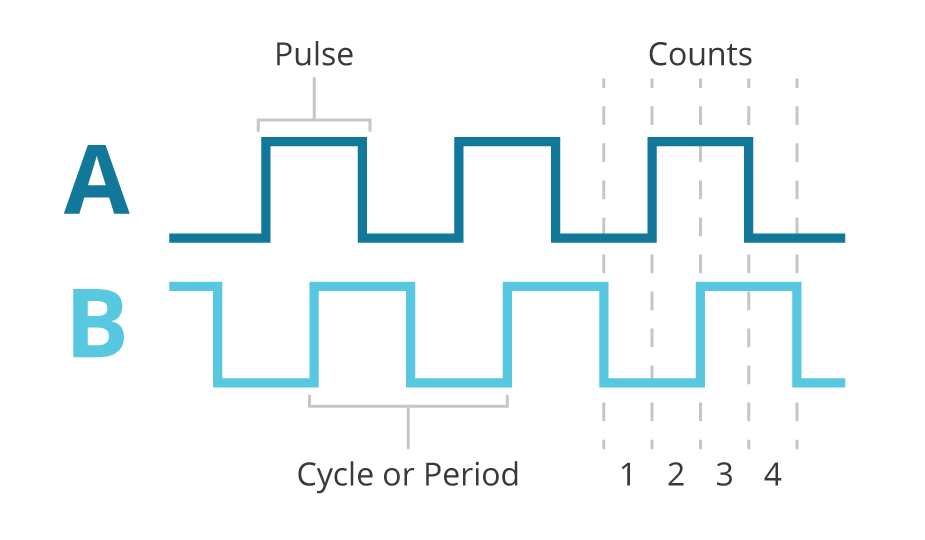
Quadrature Encoder Basics Part 1 Theory

Encoders Optical And Magnetic Incremental And Rotary
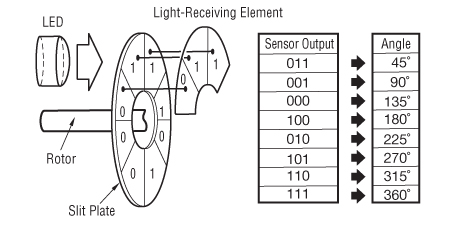
Servo Motor Glossary Of Terms
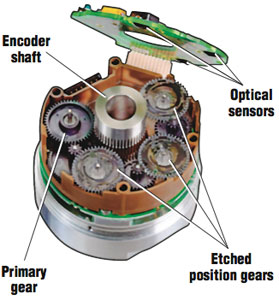
Absolute Encoders Solidswiki
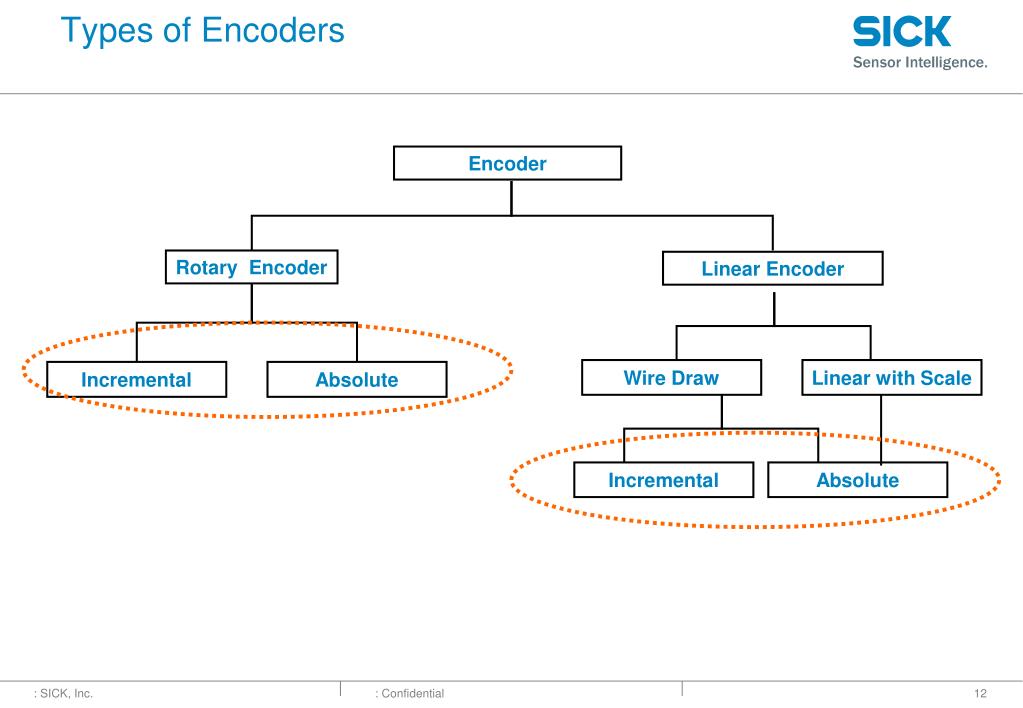
Ppt Encoders Basic Training Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Mechanical Absolute Encoder Stepper Motors Az Series

What Is Rotary Encoder And How Rotary Encoder Works Srie
Http Ichaus Biz Wp6 Magnetic Vs Optical

Encoder Videobytes Differences Between Incremental And Absolute Encoders Youtube

Faq What Types Of Linear Encoders Are There And How Do I Choose
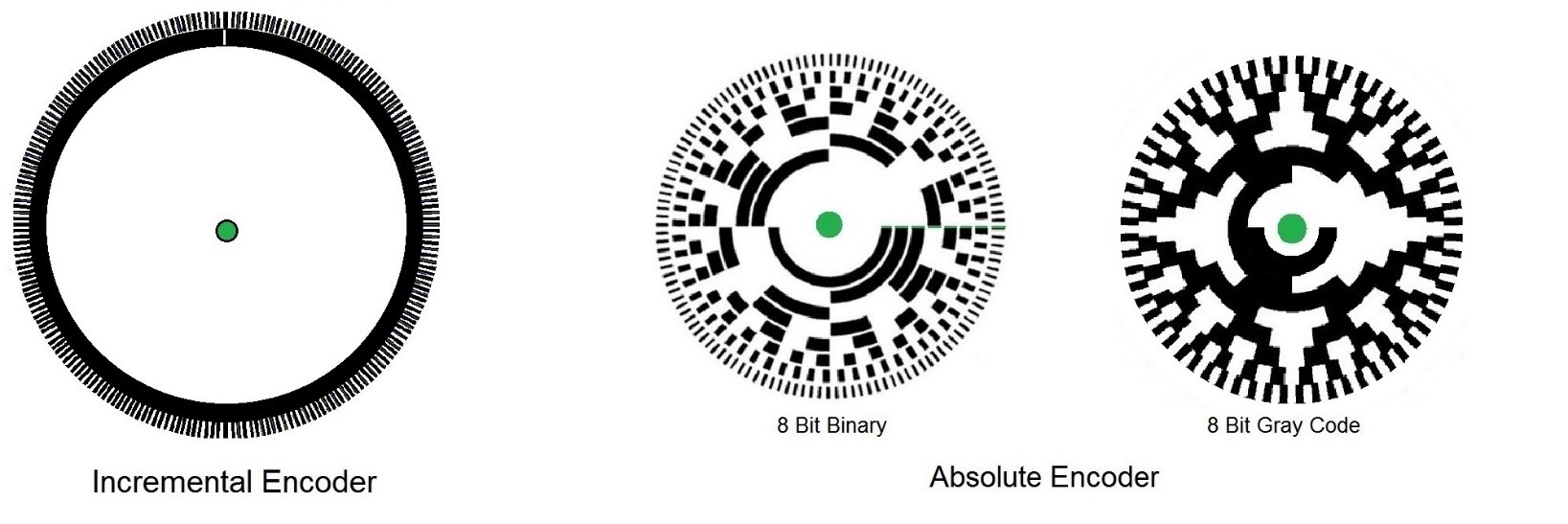
Ezautomation Industry Article High Speed Rotary Encoders
Rotary Encoder Training Material

Rotary Encoders How It Works How To Use It With Arduino Latest Open Tech From Seeed Studio
Q Tbn And9gcrghy9iknkbs Xexofjpzi85p1z21hnx0yu4qv3h Vjdzdu1jhs Usqp Cau

Types Of Encoders How To Select A Rotary Encoder Arrow Com

Absolute Vs Incremental Encoder What Is The Difference Advantages And Disadvantages

Absolute Rotary Encoders Dynapar
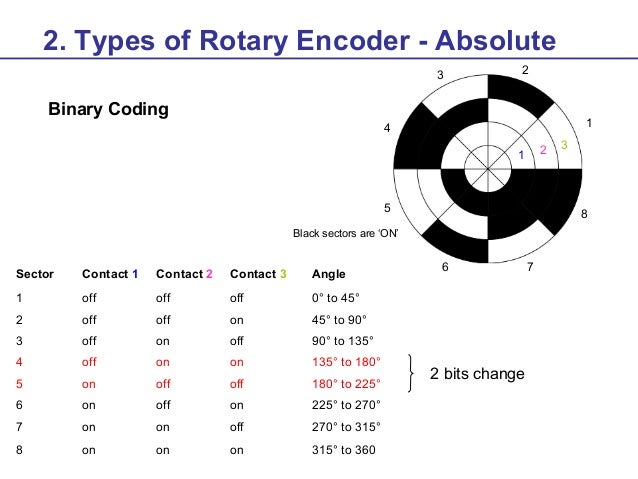
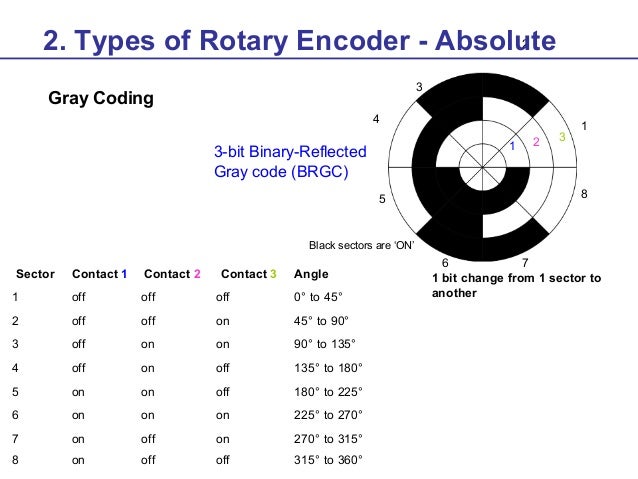
Rotary Encoder Training Material

What Is The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders Realpars

Encoders Optical And Magnetic Incremental And Rotary

03 Incremental Type And Absolute Type Basic Knowledge Of Encoder Tutorials Asahi Kasei Microdevices Akm

Encoder

What S The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders Machine Design

Absolute Rotary Encoder Sensing Technology Optical And Magnetic Automation Insights

Incremental Encoder Wikipedia
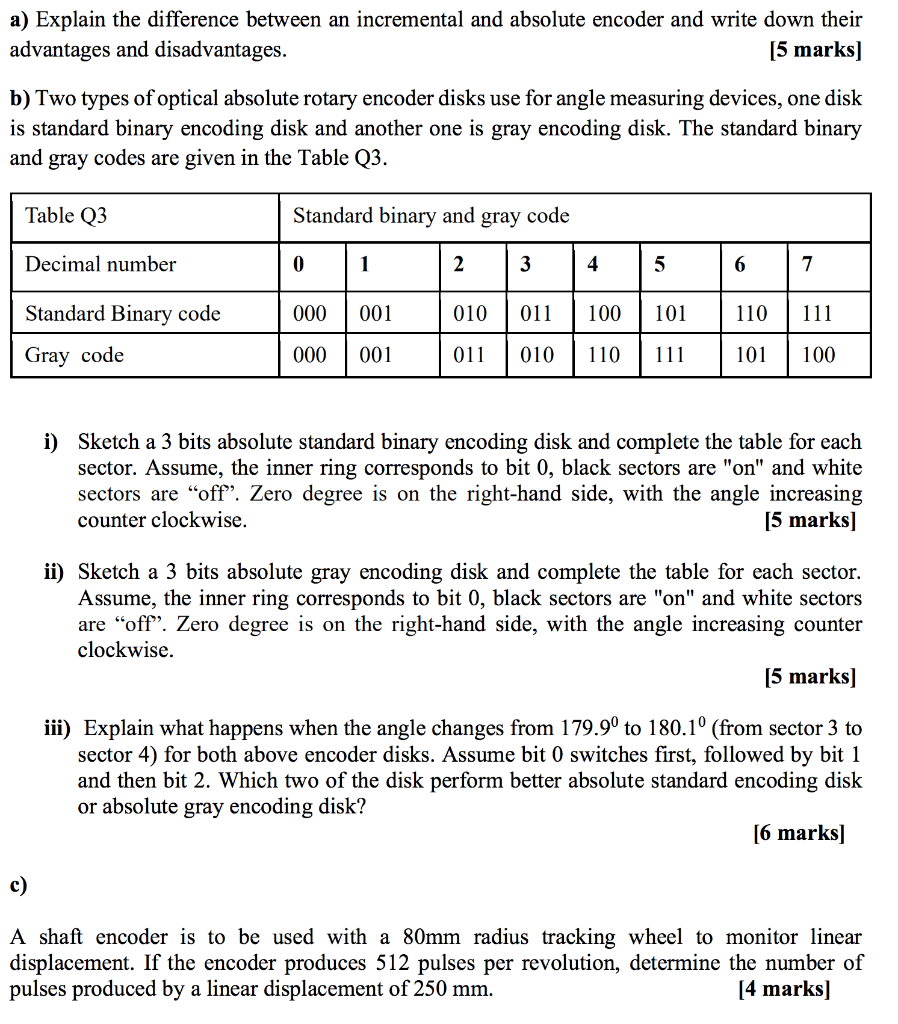
Solved A Explain The Difference Between An Incremental A Chegg Com
Q Tbn And9gctxrsn7 Fazofc7zqmtdhmn5v53djecpl8krenf9ftbd Poag Usqp Cau
.jpg)
Absolute Vs Incremental Encoder What Is The Difference Advantages And Disadvantages

What Is The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders Realpars

Pin On Research Engineering

Battery Less Absolute Encoder Built In To Rcp5 Iai America

A Look Into Rotary Encoder Types Absolute And Incremental Technical Articles

Different Types Of Encoders And Their Applications Heidenhain

What Is An Absolute Encoder Zettlex Inductive Encoders
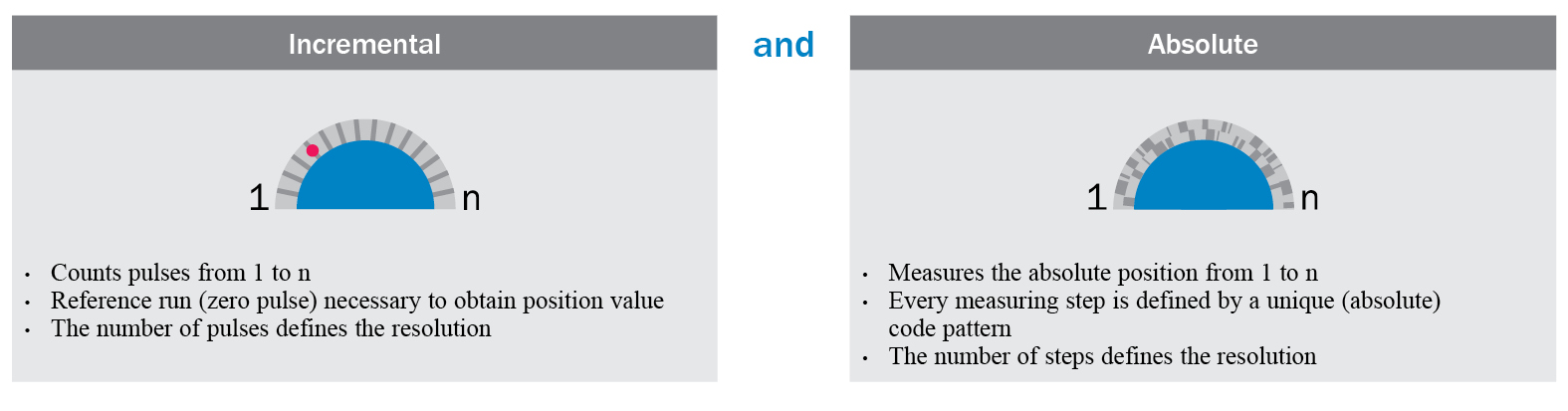
Absolute Or Incremental Encoders The Differences Explained Sick Usa Blog

What Is Rotary Encoder Construction Working Types
Smc Products

Encoders Optical And Magnetic Incremental And Rotary

Encoders Optical And Magnetic Incremental And Rotary
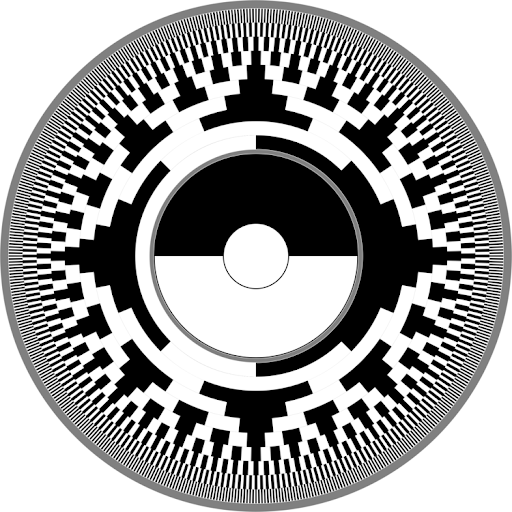
Absolute Position Encoder With Non Contact Magnetic Sensor

Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders Difference Between

Absolute Encoders Versus Incremental Encoders

Faq What Is The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders
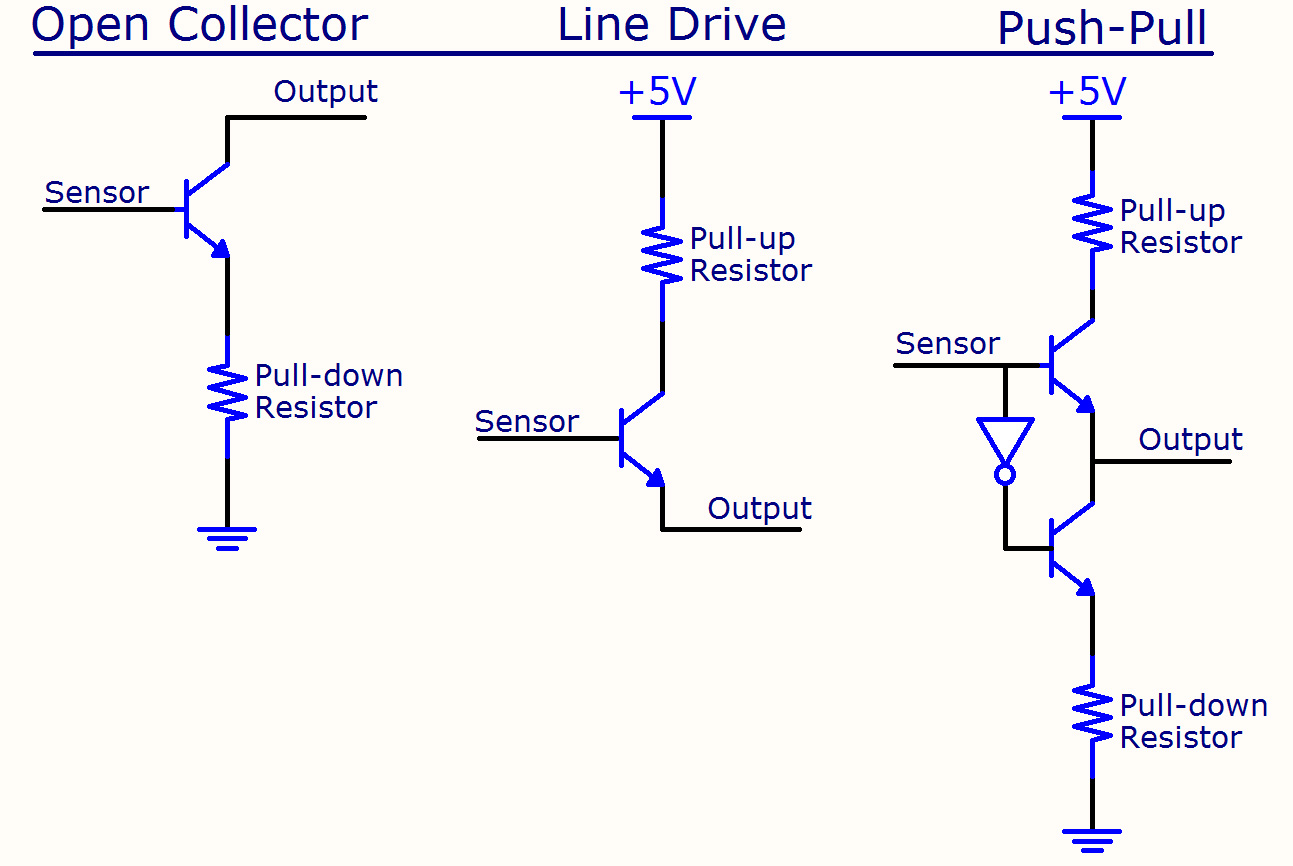
Encoder Primer Phidgets Support

03 Incremental Type And Absolute Type Basic Knowledge Of Encoder Tutorials Asahi Kasei Microdevices Akm

How Encoders Work Pca Encoders

Absolute Vs Incremental Encoder What Is The Difference Advantages And Disadvantages
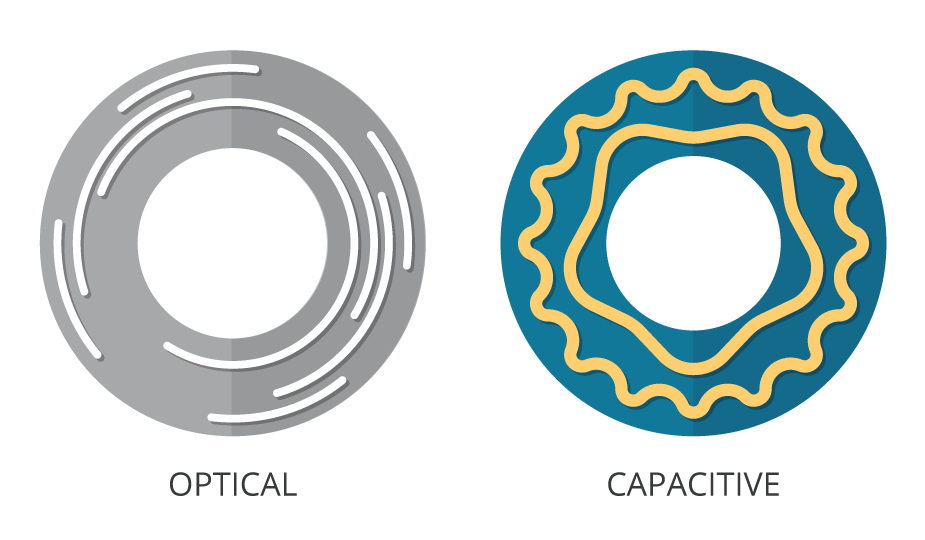
When Is An Absolute Encoder Right For Your Design Cui Devices

03 Incremental Type And Absolute Type Basic Knowledge Of Encoder Tutorials Asahi Kasei Microdevices Akm

Faq What Is The Difference Between An Absolute And Incremental Encoder Pacific Automation
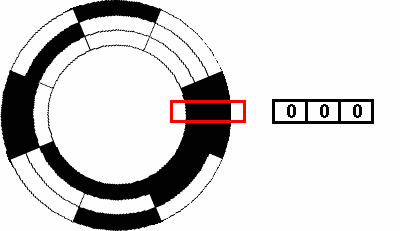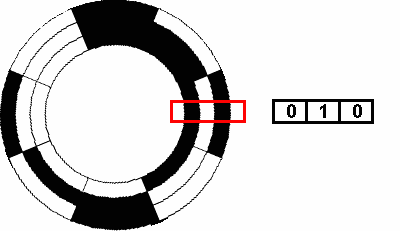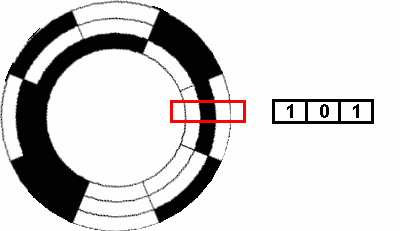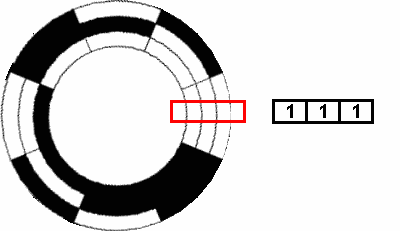
Types Of Encoders And Their Applications In Relation To Motors Blog Clr

Encoder With Arduino Rotary Encoder Absolute Encoder Incremental Optical Encoder Encoder With Arduino Electronic Clinic
Encoder Differences How To Choose Between Absolute Or Incremental

Encoders Optical And Magnetic Incremental And Rotary
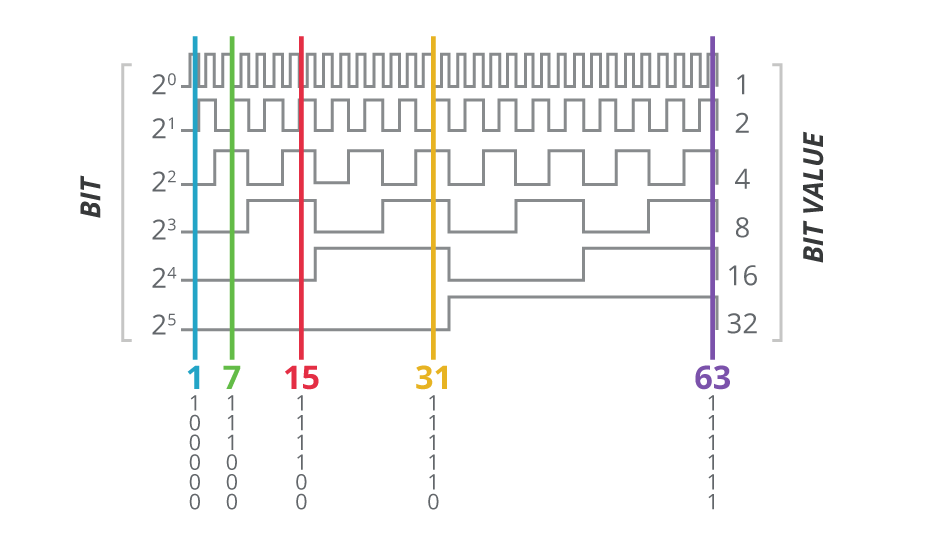
When Is An Absolute Encoder Right For Your Design Cui Devices

Absolute Rotary Encoders Dynapar

What S The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders Machine Design

Servo Motor Feedback Devices Basic Operational Theory



