Absolute Encoder Signals
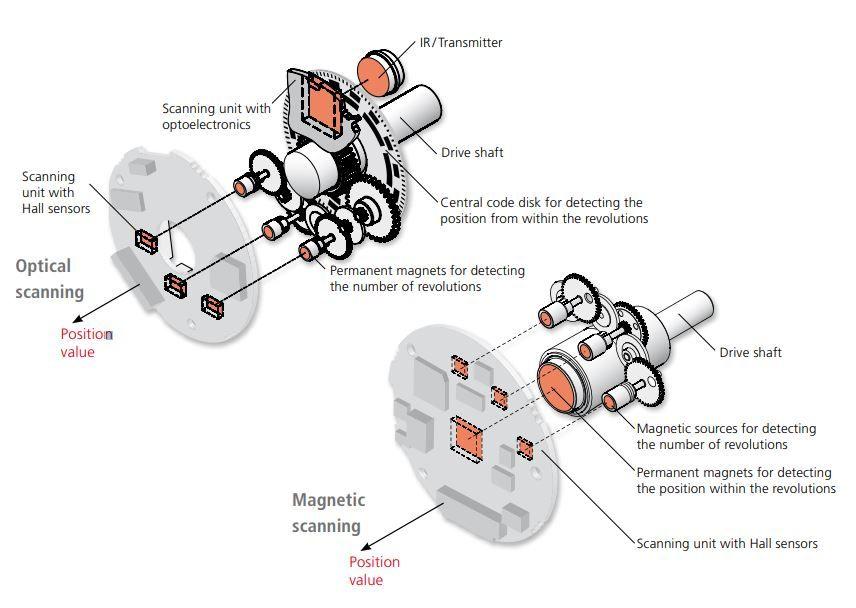
Tr Electronic Absolute Rotary Encoders Industrysearch Australia

Rotary Encoders Further Information Technical Guide Australia Omron Ia
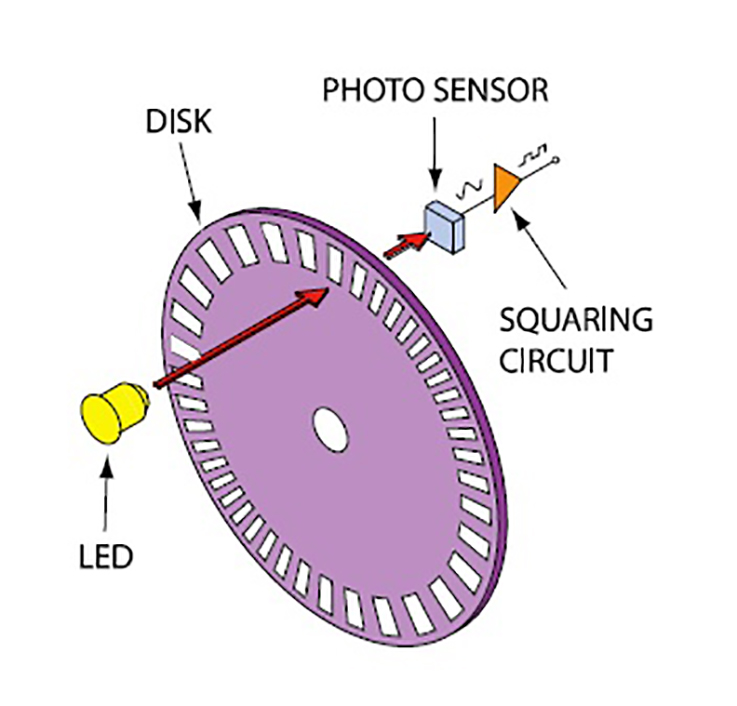
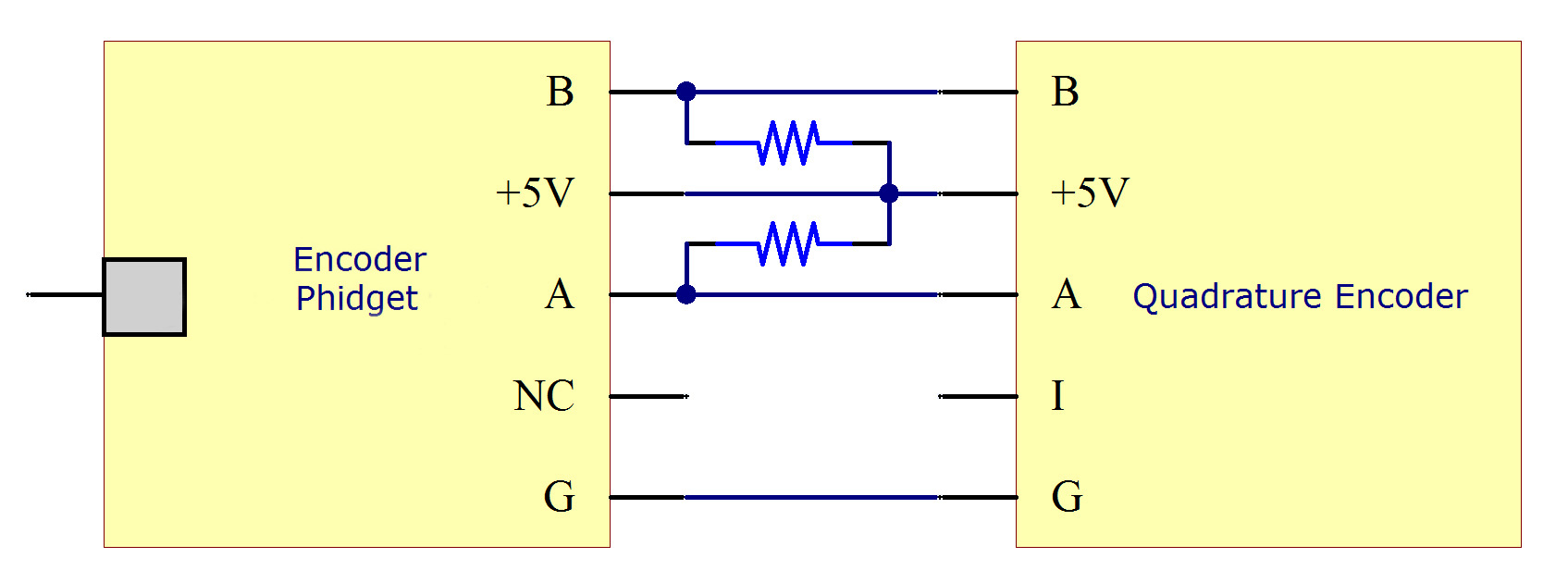
Encoder Primer Phidgets Support
Technical Definitions Industry Mall Siemens Ww

Incremental Encoder An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Using Encoders In Motion Control Automated Motion Systems Pty Ltd Australia
An encoder is an electromechanical device that can measure motion or position Most encoders use optical sensors to provide electrical signals in the form of pulse trains, which can, in turn, be translated into motion, direction, or position Rotary encoders are used to measure the rotational motion of a shaft.

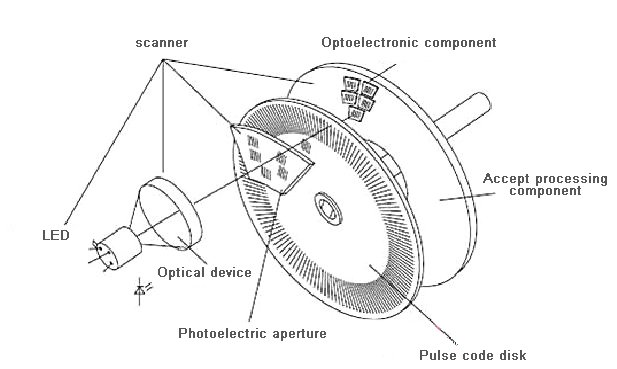
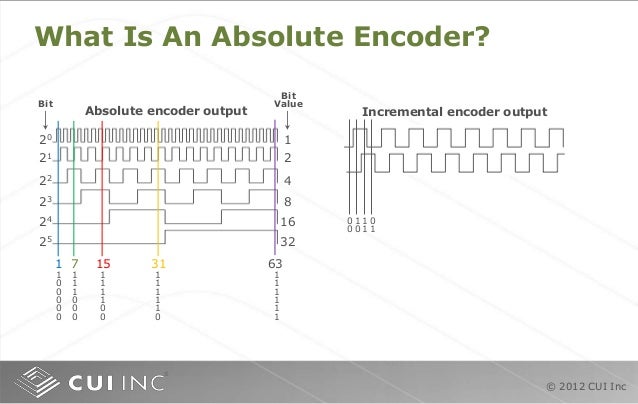
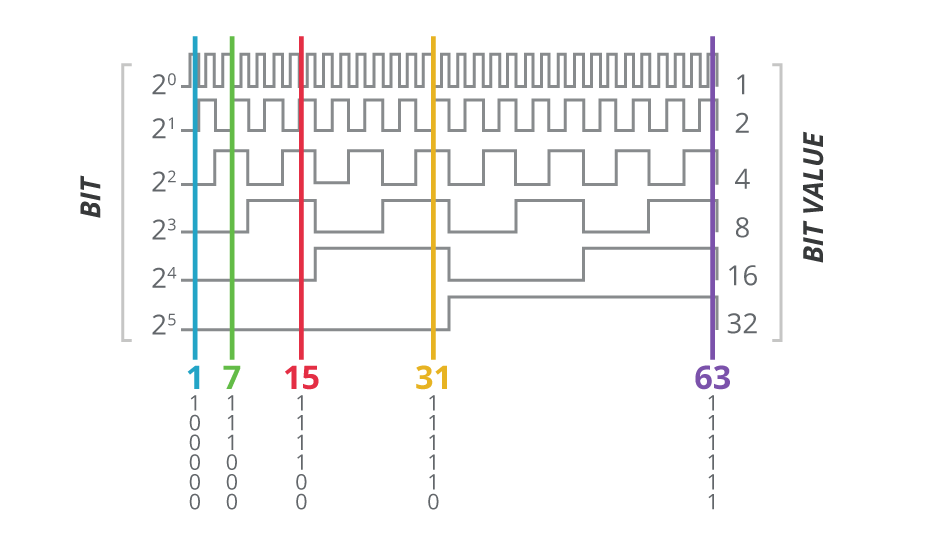
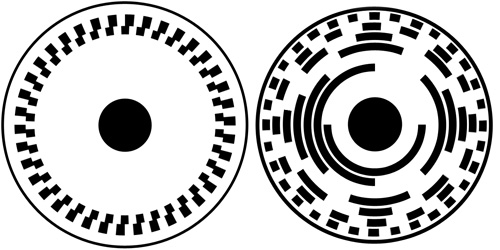
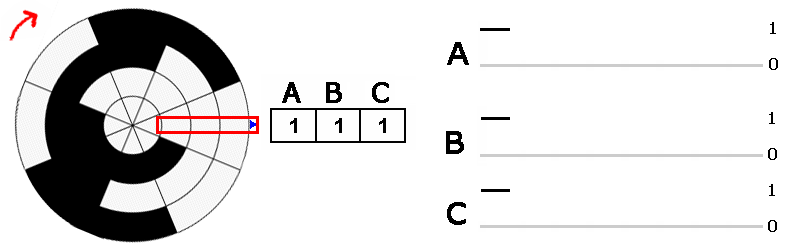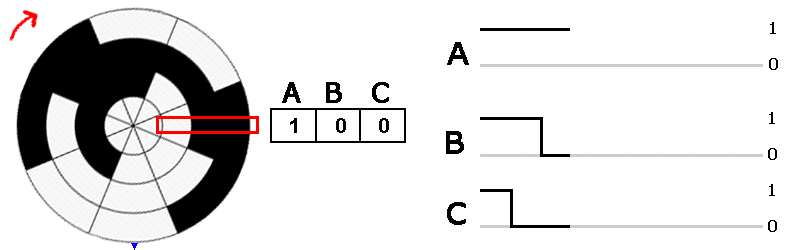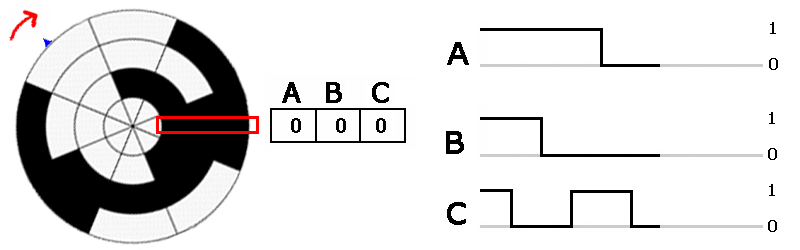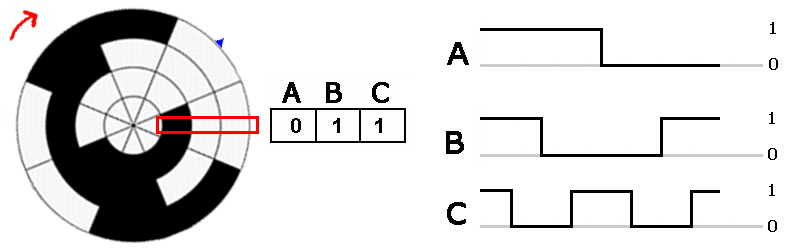
Absolute encoder signals. The incremental disc generates two square wave signals with a 90˚ phase difference between them The absolute disc outputs binary encoded data (Image source DigiKey Electronics) The absolute disc in Figure 1 has four outputs providing a unique binary code for each segment on the disc, sixteen in this case (Table 1). These sensors transform a mechanical angular position of a shaft or axle into an electronic signal that can be processed by a control system Absolute Rotary Encoders Absolute rotary encoders are capable of providing unique position values from the moment they are switched on. An absolute encoder providing a multibit output binary code indicative of the position of a rotary or linear scale The encoder employs a code track, which contains a serial code, and a clock track Single track absolute encoder Dynamics Research Corporation.
To generate a signal that is sent to a controller to have the machinery perform its specific function They have their different capabilities which is what leads to the many different types of encoders. For more than 50 years, Encoder Products Company (EPC) has provided topquality motion feedback devices, with exceptional customer service and fast delivery At EPC, we are still filling most orders in 4 to 6 business days – that's days, not weeks. Depending on the device and manufacturer, an absolute encoder may use any of several signal types and communication protocols to transmit data, including parallel binary, analog signals (current or voltage), and serial bus systems such as SSI, BiSS, Heidenhain EnDat, SickStegmann Hiperface, DeviceNet, Modbus, Profibus, CANopen and EtherCAT, which typically employ Ethernet or RS422/RS485 physical layers.
Absolute optical encoders employ signalprocessing components similar to those of the quadrature optical encoder, but their outputs produce one parallel binary word per increment of revolution. The typical absolute encoder device g enerates sin/cos signals of period equal to one revolution While this provides absolute information, resolution is limited compared to the many thousand s of sin/cos cycles generated by an incremental encoder. Encoders that use the absolute measuring method output position values Some interfaces provide incremental signals as well Since absolute encoders do not require a reference run, they are particularly advanta geous in concatenated manufacturing systems, transfer lines, and multiaxis machines They are also highly immune to EMC interference.
UVW signals are available in 1 to 16 pole pairs to fit different BLDC motor requirements C50MA absolute encoder can be equipped with SSI and BiSS Cmode serial communication protocols It can be both singleturn and multiturn The singleturn resolution ranges between 15 and 19 bits (up to 524,2 cpr);. There are two types of rotary encoders an incremental type representing a relative angle and an absolute type representing an absolute angle We will explain these principle, mechanism, advantages and disadvantages with an optical encoder as an example in an easytounderstand manner Part 3 of an encoder technical tutorial series by Asahi Kasei Microdevices (AKM). Absolute Encoders Reference The communication protocol you choose for your application will determine the communication protocol of the encoders in that system Read below for more information about the communication protocols available with EPC's line of absolute encoders.
The incremental resolution is in the range 1 to 65,536 PPR UVW signals are available in 1 to 16 pole pairs to fit different BLDC motor requirements C50MA absolute encoder can be equipped with SSI and BiSS Cmode serial communication protocols It can be both singleturn and multiturn The singleturn resolution ranges between 15 and 19 bits (up to 524,2 cpr);. Third and fourth light sensing elements for sensing light from said second light emitting diode;. When it comes to choosing an encoder for a motion control application there are a number of choices that need to be made An engineer specifying a sensor must decide if their application requires an incremental, absolute, or commutation encoder Once they know what type they need there are a laundry list of other parameters to consider such as resolution, mounting pattern, motor shaft size.
The typical absolute encoder device g enerates sin/cos signals of period equal to one revolution While this provides absolute information, resolution is limited compared to the many thousand s of sin/cos cycles generated by an incremental encoder. Encoder signal outputs are generated by a rotary encoder when the shaft or bore rotates Incremental encoders generate a set number of pulses per revolution while an absolute encoder generates a stream of bits corresponding to discrete position The performance of an incremental encoder is only as good as its signal. An absolute encoder generates digital messages which represent the current encoder position as well as its speed and direction of movement If the power is lost, its output will be corrected each time the power is restored It is not necessary to go to a reference position as with incremental encoders.
Absolute encoders are rotary encoders that measure angles, convert this information into electrical signals and output them as absolute values The use of electronics for measured value processing differentiates them from potentiometers, which also provide absolute values, but are passive components without integrated electronics. The absolute angle detection type encoder outputs the current absolute angle in a digital serial code or an analog voltage in response to instructions from the microcomputer Such an output way is called an absolute method Here again, we will explain its operation with the optical encoder as an example. As discussed, the incremental encoder won’t detect the absolute position of the encoder, but only changes in position We can, however, use an incremental encoder interface to determine the absolute position if necessary Absolute Encoder An absolute encoder will detect the absolute position information of the encoder even when it has no power In such cases, when power is restored, the position information of the encoder is available immediately.
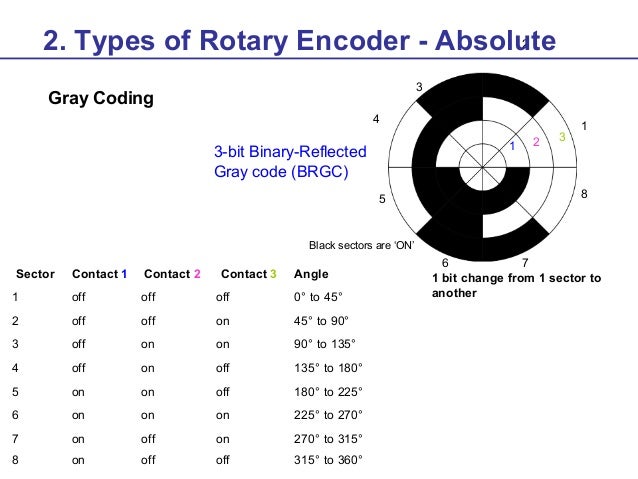
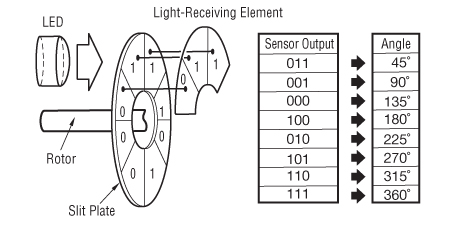
The number of revolutions is 65,536. Encoder The motors are equipped with a SinCos encoder The drive can access the electronic nameplate via the Hiperface interface for commissioning The signals meet the PELV requirements SKS36 Singleturn This motor encoder measures an absolute value within one revolution at startup and continues to count incrementally from this point. The output signal generated from an absolute encoder is in digital bits which correspond to a unique position The bit configuration is produced by the light which is received by the photodetector when the disk rotates The light configuration received is translated into gray code As a result, each position has its own unique bit configuration.
Absolute Encoders Absolute Encoders retain your position data during loss of power They are excellent choices in systems that require failsafe operation assembly to produce a concentrated beam of light that passes through a code disk and is sensed as high level optical signals. The absolute rotary encoder is a remote bus user The individual users are connected by an installation remote bus cable This cable carries both the bus line coming from the master and the return line. Incremental and absolute encoders can be further broken down into optical or magnetic Each of these encoders have a similar goal;.
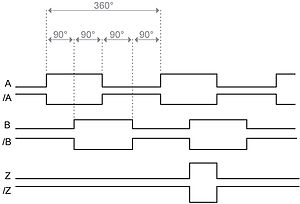
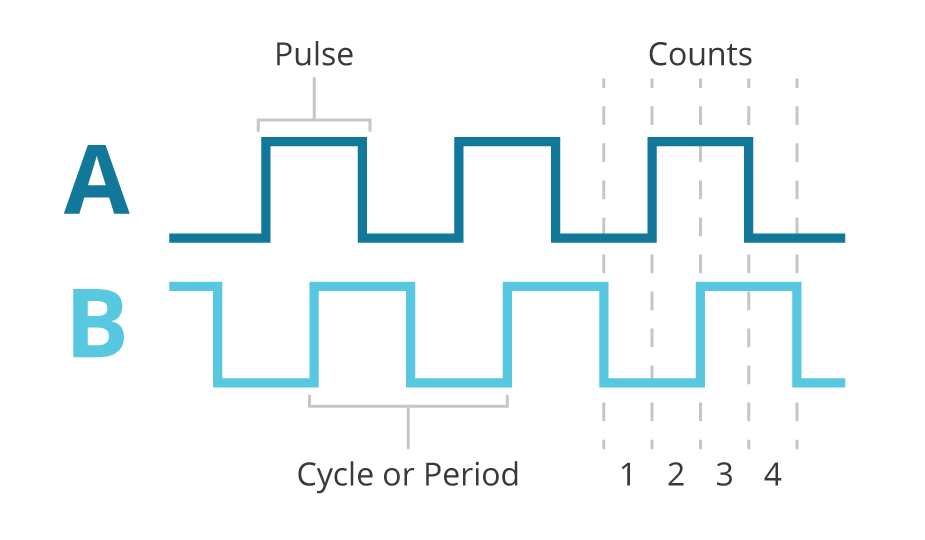
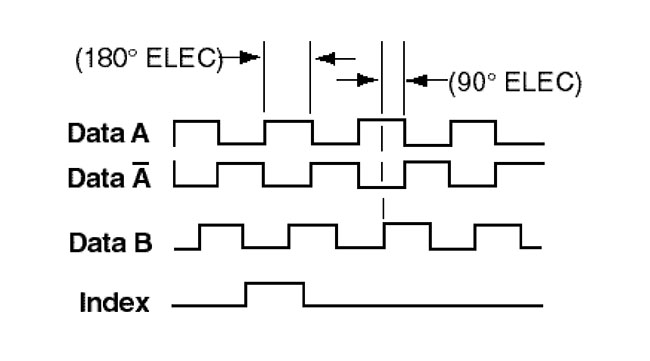
A simple absolute encoder can provide parallel, discrete output signals, often in a Gray code format, that can be monitored by a PLC's standard dc inputs No homing routine is required for the encoder to know position. The main difference is that an absolute encoder will detect the absolute position of the encoder, while incremental encoders will only detect changes in movements Incremental Encoder An incremental encoder has two output signals A and B, which are quadratureencoded. – Both are electromechanical devices used to measure either angular or linear positions of the shaft and convert them into digital or pulse signals An absolute encoder has a unique code for each shaft position which represents the absolute position of the encoder, while an incremental encoder generates an output signal each time the shaft rotates a certain angle and the number of generated pulses is proportional to the angular position of the shaft.
If it outputs its true position without motion then it is absolute Absolute encoders typically output either a digital data stream, such as serial synchronous interface (SSI) or an analogue signal such as 010V or 4mA Incremental encoders typically output pulses which are often described as A/B pulse or ‘A quad B’ encoders. Encoder signals, absolute encoder (SSI) • Input signal 5 V difference signal (phys RS 422) • Clock frequency, max 125 Mbit/s at 10 cable length (25 Mbit/s available soon) • Cable length, shielded, max 250 m;. Apart from (incremental) quadrature encoders, ODrive also supports absolute SPI encoders (since firmware v05) These usually measure an absolute angle This means you don’t need to repeat the encoder calibration after every ODrive reboot.
Absolute encoders utilize stationary mask in between the photodetector and the encoder disk as shown below The output signal generated from an absolute encoder is in digital bits which correspond to a unique position. The signal converters shown here serve special requirements such as, for example, the conversion of absolute SSI encoder signals into an analog standard signal as well as into a serial or parallel format Here you will also find the appropriate product for the conversion of parallel BCD, binary or Gray codes into serial formats. Analog encoders generally have a single output and encode the position in a 4ma or 010V signal My guess is that what you have is indeed already a quadrature encoder and not an analog encoder I think the sine wave is probably the signature of a lower cost encoder.
Absolute encoders generate information about position, angle, and rotation counts in typespecific angle steps For this, a unique code pattern is assigned to each angle increment The number of code patterns available per revolution determines the resolution Each code pattern forms a unique reference, and is therefore an absolute position. If it outputs its true position without motion then it is absolute Absolute encoders typically output either a digital data stream, such as serial synchronous interface (SSI) or an analogue signal such as 010V or 4mA Incremental encoders typically output pulses which are often described as A/B pulse or ‘A quad B’ encoders. An absolute encoder provides a unique position value or data word at every point of rotation representing the “absolute” position of the encoder From the moment you switch it on, an absolute encoder can tell you the exact position of the rotating shaft that it is measuring A Comparison of Common Encoder Output Signals CUI Insights.
Absolute encoders generate information about position, angle, and rotation counts in typespecific angle steps For this, a unique code pattern is assigned to each angle increment The number of code patterns available per revolution determines the resolution Each code pattern forms a unique reference, and is therefore an absolute position. Absolute encoders have an encoder disc (sporting marks or slots) on a powertransmission shaft and a stationary pickup, but the disc marks output a unique code for each shaft position Absolute encoders are either singleturn or multi turn encoders Single turn absolute encoders can verify position within a single turn of the encoder shaft. – Both are electromechanical devices used to measure either angular or linear positions of the shaft and convert them into digital or pulse signals An absolute encoder has a unique code for each shaft position which represents the absolute position of the encoder, while an incremental encoder generates an output signal each time the shaft rotates a certain angle and the number of generated pulses is proportional to the angular position of the shaft.
In a Rotary “Absolute” measurement type encoder, a slotted disc on a shaft is used in conjunction with a stationary pickup device When the shaft rotates, a unique code pattern is produced This means that each position of the shaft has a pattern and this pattern is used to determine the exact position. At max 156 kbit/s Article number 6ESAH000AE0 FM 453 positioning module © Siemens AG 17. An absolute encoder provides a unique position value or data word at every point of rotation representing the “absolute” position of the encoder From the moment you switch it on, an absolute encoder can tell you the exact position of the rotating shaft that it is measuring.
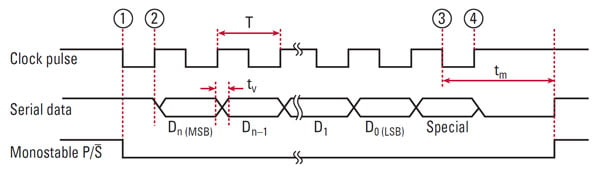
Basics of Absolute Encoders ACURO SynchronousSerial Interface (SSI) 360ENCODERSCOUNTERS INDICATORS RELAYS PRINTERS CUTTERS With the first shift of the clock signal from low to high ②the most significant bit (MSB) of the angular data is applied to the shaft encoder’s serial output. Absolute encoder is a feedback device that provides a unique positional data of a rotating shaft or a linear sliding unit, used in applications including robotics, CNC machining, measurement systems, surveying instrument, and astronomical apparatus absolute encoder A bsolute encoders operate with the same principles by which incremental encoders work, however, while incremental encoders provide only the changes in position, using which displacement and velocity values of rotation are. An encoder includes a scale and a sensor The scale has first and second absolute patterns The sensor includes a light source, and first and second absolute light receivers The first and second absolute light receivers receive light from the first and second absolute patterns, respectively The first absolute light receiver receives light from the first pattern and includes first and second.
Technology Update New design and signal evaluation improve capabilities of absolute rotary encoders, offering high resolution and accuracy of optical absolute encoders with the ruggedness and compact size of magnetic encoders. The number of signals (pulses) per turn defines the resolution of the device The incremental encoder does not output an absolute position, which makes the internal components of the encoder much simpler and more economical Besides position tracking, incremental encoders are often used to determine velocity. The information is presented in the output form of digital signals Encoders come in two types absolute and incremental encoders Absolute encoders give an absolute position because of the unique code pattern assigned to each angle increment, The code pattern is used to reference a specific position to a control unit.
Absolute encoder is a feedback device that provides a unique positional data of a rotating shaft or a linear sliding unit, used in applications including robotics, CNC machining, measurement systems, surveying instrument, and astronomical apparatus absolute encoder Absolute encoders operate with the same principles by which incremental encoders work, however, while incremental encoders.

What Is Ttl Output For Incremental Encoders Motion Control Tips

Faq What Are The Ways To Wire An Absolute Encoder Into A Motion System
Rotary Encoder Basics And Applications Part 1 Optical Encoders
Q Tbn And9gcq5 Uhjdhn Ji7o Kjbatmdi31wlwpwnhtdlshikbgwusyhyy5o Usqp Cau
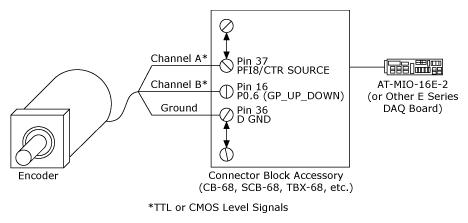
Using Quadrature Encoders With E Series Daq Boards National Instruments

Incremental Encoder Selection Robots For Roboticists
Rotary Encoder Training Material
Servo Motor Glossary Of Terms
Encoder Primer Phidgets Support

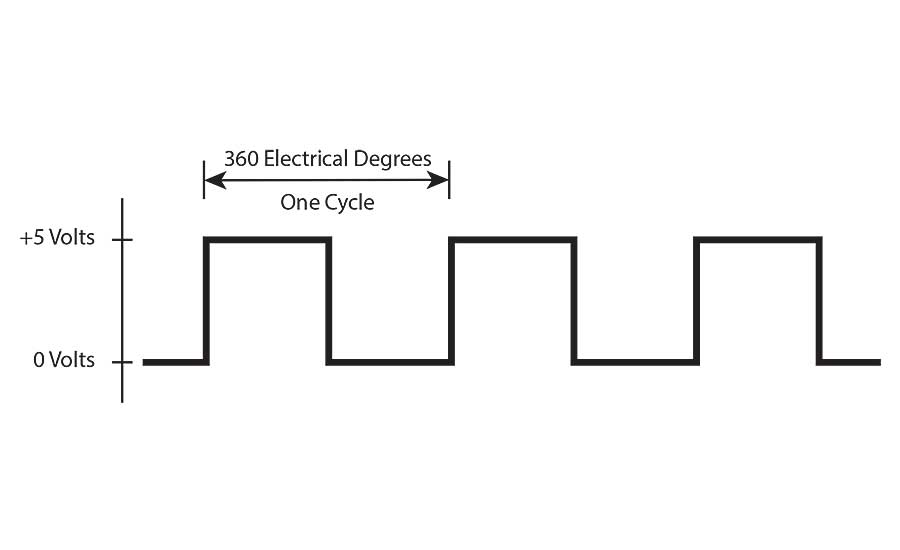
Quadrature Encoder Basics Part 1 Theory
Encoders Explained Library Automationdirect Com

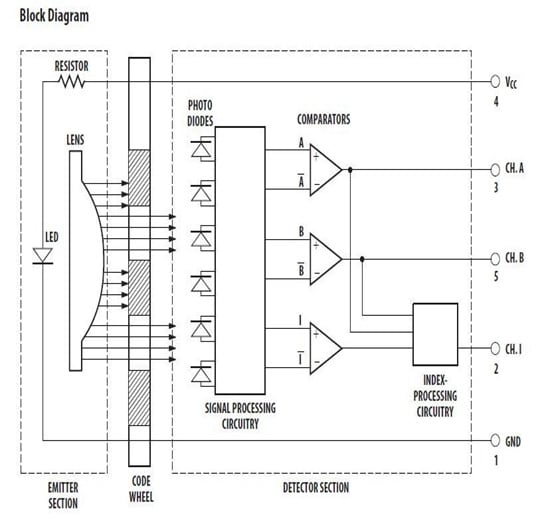
Motion Sensing Via Rotary Shaft Encoders Digikey

Beckhoff Information System English

How To Estimate Encoder Velocity Without Making Stupid Mistakes Part I Jason Sachs

Incremental Encoder Wikipedia

S3d5sbrayim72m

The Difference Between Incremental Encoder And Absolute Encoder Midori America Corporation
What S The Difference Between Absolute And Incremental Encoders Yueqing Yumo Electric Co Ltd
Incremental Encoder Wikipedia

Feedbacks Everest Xcr

Principle Of Single Track Absolute Encoder Download Scientific Diagram

Incremental Encoder An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Incremental Encoder An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Encoder Primer Phidgets Support

Encoders Resolvers Applications And Replacements From Nidec Avtron Encoders Nidec Avtron Automation
When Is An Absolute Encoder Right For Your Design Cui Devices
Www Nidec Netherlands Nl Media 3956 Engineering Documentatie Technical Guide Leroy Somer Speed And Position Feedback Devices En 1810 A 5664a Pdf
Totally Encapsulated J1 Rotary Encoders Ip69k Electrical Protection From Joral

03 Incremental Type And Absolute Type Basic Knowledge Of Encoder Tutorials Asahi Kasei Microdevices Akm

Position Sensor And Linear Positional Sensors

Linear Encoder Wikipedia
Www Faulhaber Com Fileadmin User Upload Global Support Mc Support Drive Electronics Appnotes Faulhaber An158 En Pdf

Linear Encoder Archives Automation Insights

Encoders Optical And Magnetic Incremental And Rotary
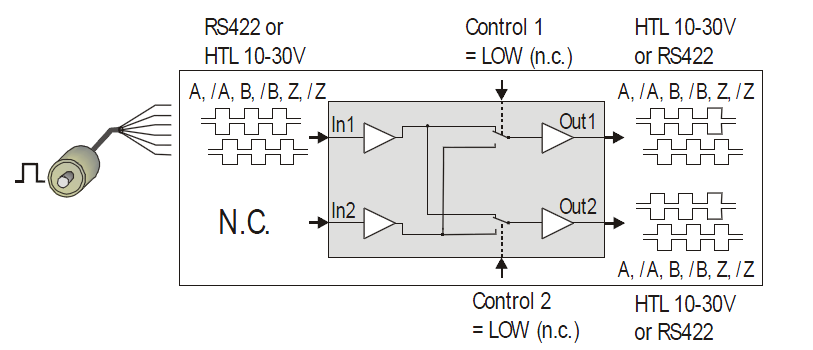
Hm210gv Encoder Signal Converter Hohner Automazione Srl
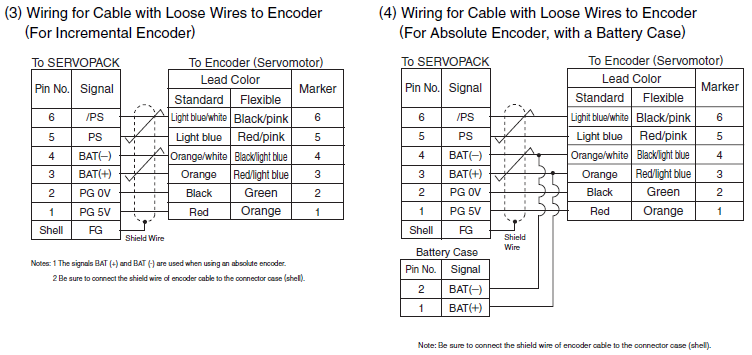
Using Absolute Vs Incremental Encoder Cables Sigma Iii And Higher

Feedback Connections Jupiter

Frequently Asked Questions

How Encoders Work Pca Encoders
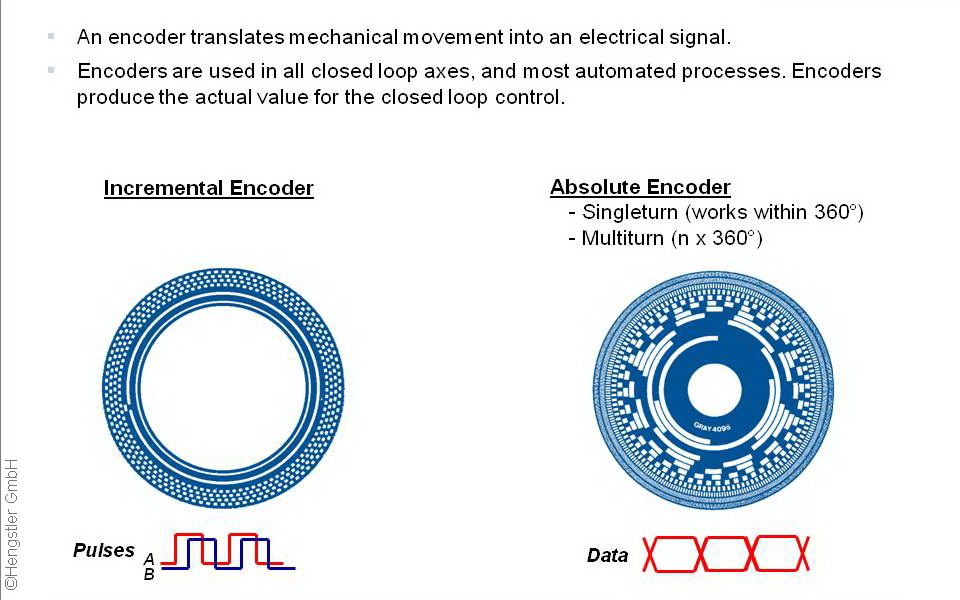
Encoder Definition
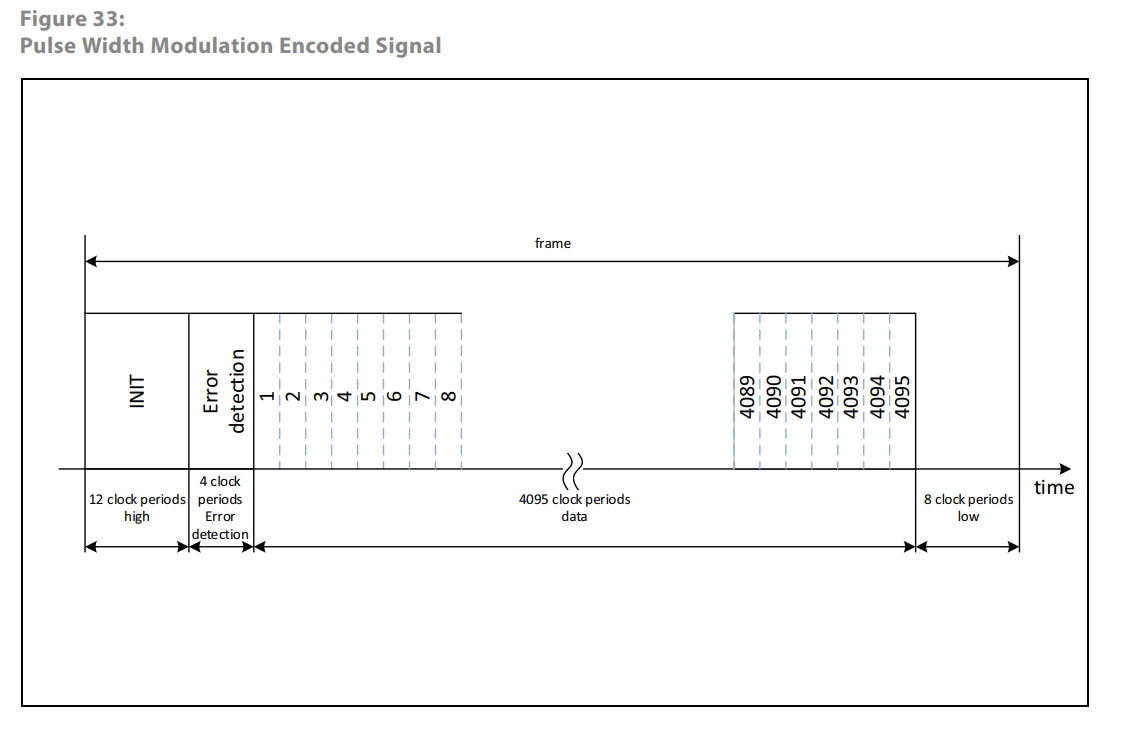
Another Take On The As5047p Encoder Pwm Absolute Position Odrive Community

Capacitive Absolute Encoders Cui Devices
Absolute
When Is An Absolute Encoder Right For Your Design Cui Devices
Encoder Signal Overview Troubleshooting Common Issues Dynapar
Encoder Primer Phidgets Support

How To Estimate Encoder Velocity Without Making Stupid Mistakes Part I Jason Sachs
Ssi Encoders Encoder Interface Protocols Dynapar

Encoders India Absolute Rotary Encoders Incremental Rotary Encoders Rotary Encoders Manufacturer Rotary Encoders Exporter Rotary Encoders Supplier Rotary Encoders India Rotary Encoders Asia
Rotary Encoder Northwestern Mechatronics Wiki

Encoders Software First Robotics Competition Documentation

Scheme Of A Absolute Encoder Within A Geometrical Approach For A Download Scientific Diagram

Basics Of Rotary Encoders Overview And New Technologies Machine Design

Servo Motor Feedback Devices Basic Operational Theory

Encoders Optical And Magnetic Incremental And Rotary
Rotary Encoders Critical To Successful Motion Control Implementation Mouser
Resolution Accuracy And Precision Of Encoders 19 09 11 Assembly

How Encoders Work Pca Encoders

Absolute Encoders Youtube
Q Tbn And9gcrhpqv7niont Au6dfon3nla 8vhh698mixtqzhwn9g341hwl6u Usqp Cau

Capacitive Absolute Encoders Cui Devices

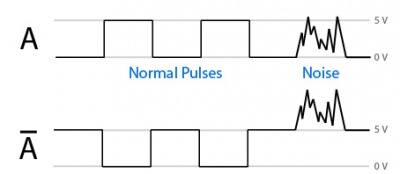
Mitigating Encoder Noise With Complementary Signals

Encoders Resolvers Applications And Replacements From Nidec Avtron Encoders Nidec Avtron Automation

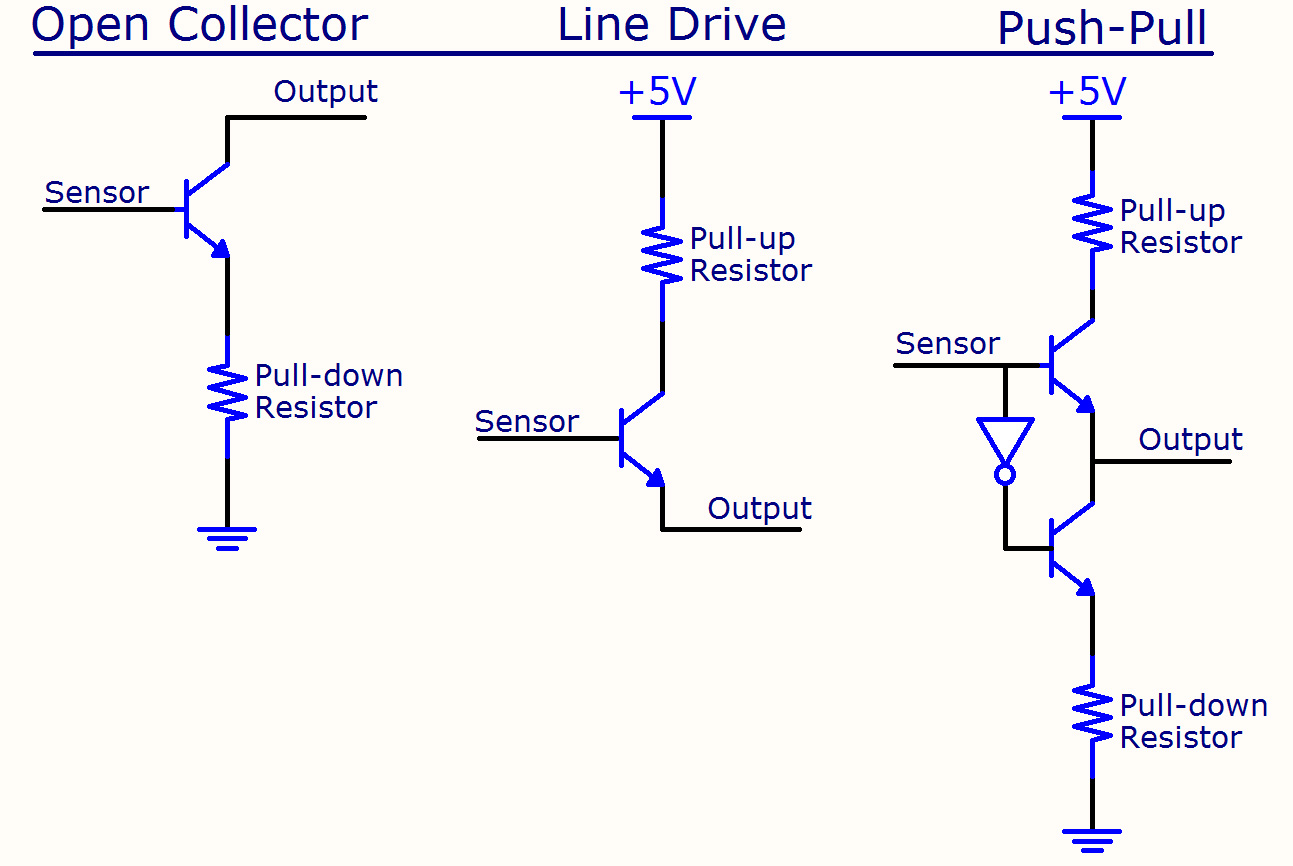
Incremental Encoder Signals Htl Push Pull Or Ttl Rs422
Encoders

What Is A Sine Encoder Aka Sine Cosine Encoder
How Can I Use An Absolute Encoder With Ni Softmotion National Instruments

Feedback Connections Jupiter
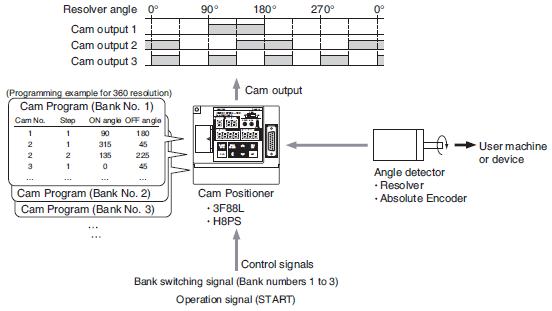
Overview Of Cam Positioners Omron Industrial Automation

The Basics Of Encoder Selection Tech Briefs

Incremental Encoder Wikipedia
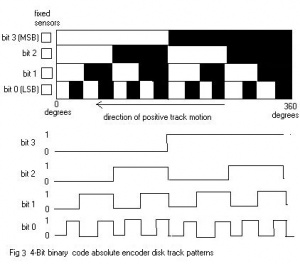
Rotary Encoder Northwestern Mechatronics Wiki
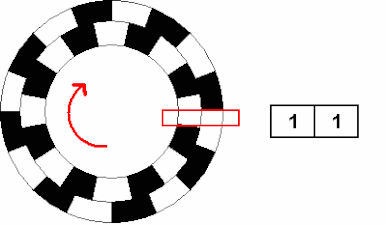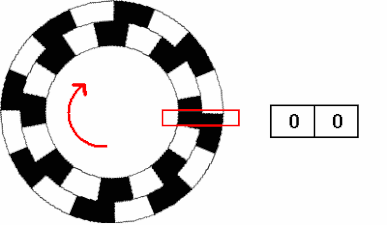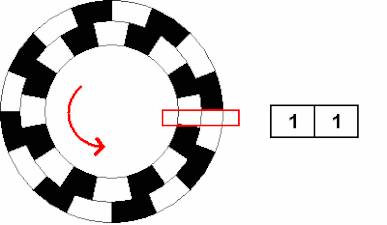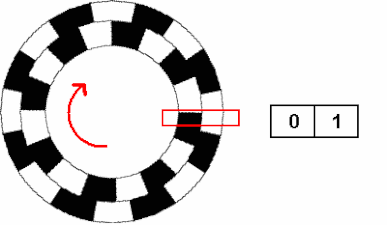
Incremental Encoder Wikipedia

Incremental Encoder Signals Htl Push Pull Or Ttl Rs422

Feedback Connections Titan

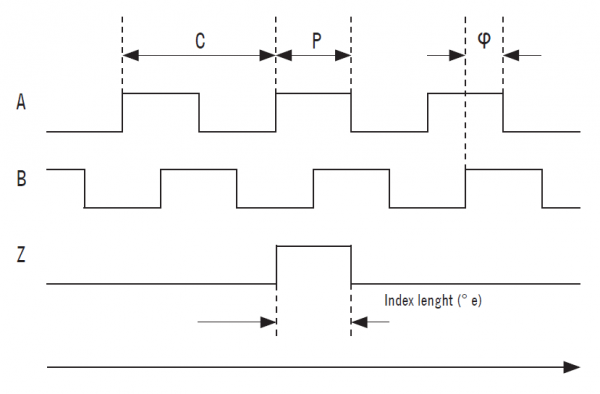
Encoder Signals
Resolved Tms3f279d Using The Clb Convert The Input Absolute Encoder Signal To Incremental Signal And Output It C00 Microcontrollers Forum C00 Microcontrollers Ti E2e Support Forums
A Shaft Encoder Vs An Absolute Shaft Encoder
What Is A Rotary Incremental Encoder And Hall Effect

What Do Lissajous Figures Tell Us About Encoder Output
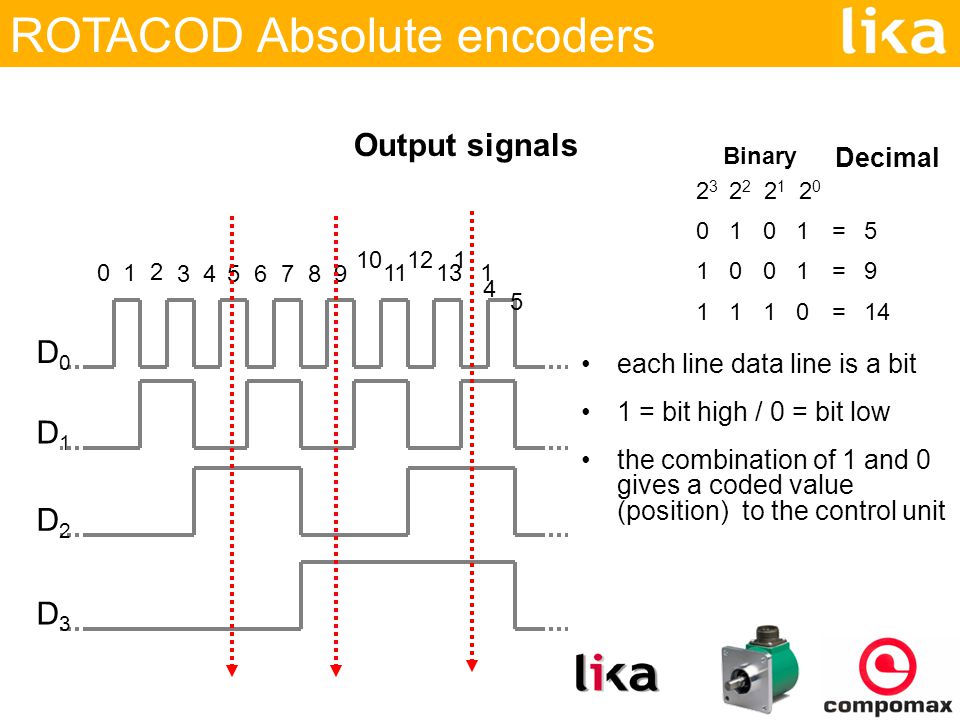
Rotacod Absolute Encoder Ppt Video Online Download
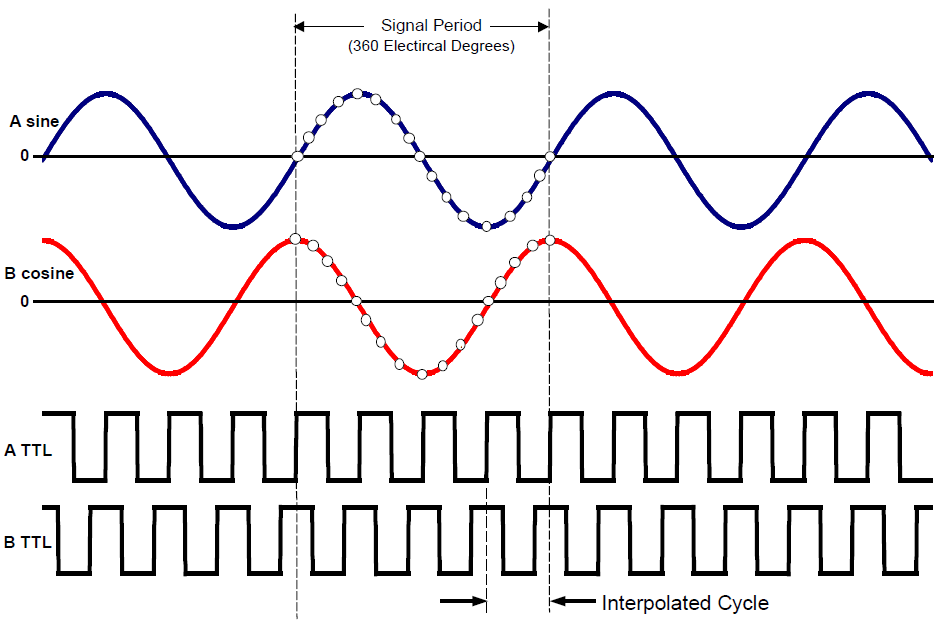
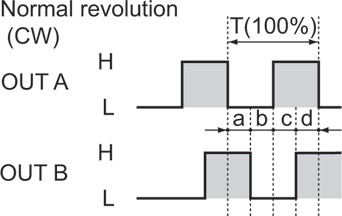
Incremental Encoder Incremental Encoder Output
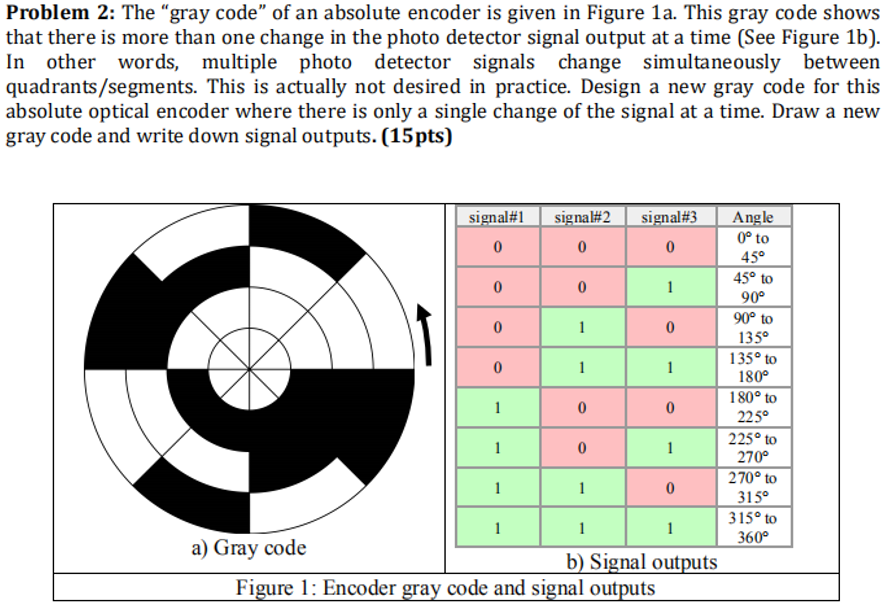
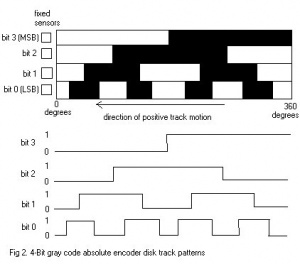
Solved Problem 2 The Gray Code Of An Absolute Encoder Chegg Com

The Basics Of Encoder Selection Tech Briefs
Q Tbn And9gctbgs M2ougrt4xyixq A5ivdxhombpl28 Gggydkk Qrvw3wqs Usqp Cau

Rotary Encoder Absolute Encoder Av6a

Encoders The Pulse Of Motion

How To Estimate Encoder Velocity Without Making Stupid Mistakes Part I Jason Sachs

Difference Between Incremental And Absolute Encoders Hohner Automazione Srl
Q Tbn And9gcsbgvxxdg Fgd0vesdzm47wwi6fjnfgiovkxmmkaap6plryp3pm Usqp Cau

Incremental Encoder Signals Htl Push Pull Or Ttl Rs422
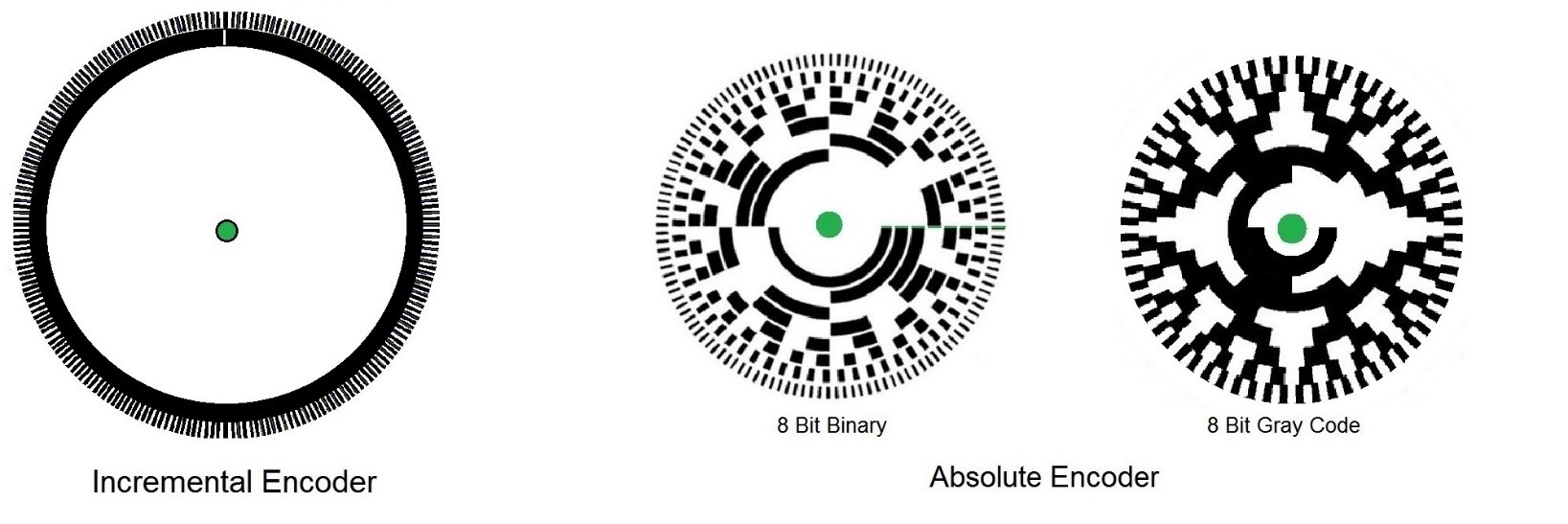
Ezautomation Industry Article High Speed Rotary Encoders

Encoders The Pulse Of Motion
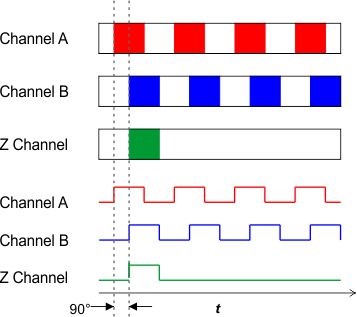
How To Select The Right Encoder For Your Moti

03 Incremental Type And Absolute Type Basic Knowledge Of Encoder Tutorials Asahi Kasei Microdevices Akm
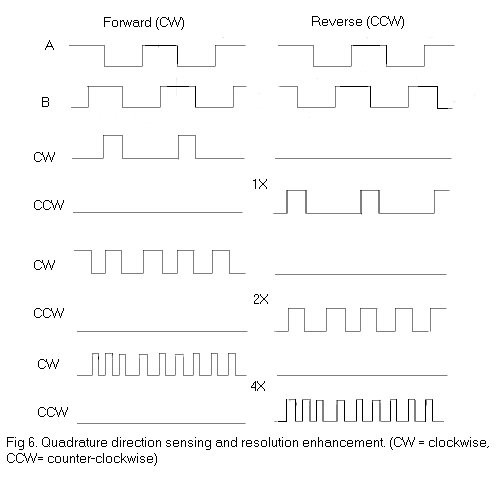
Rotary Encoder Northwestern Mechatronics Wiki
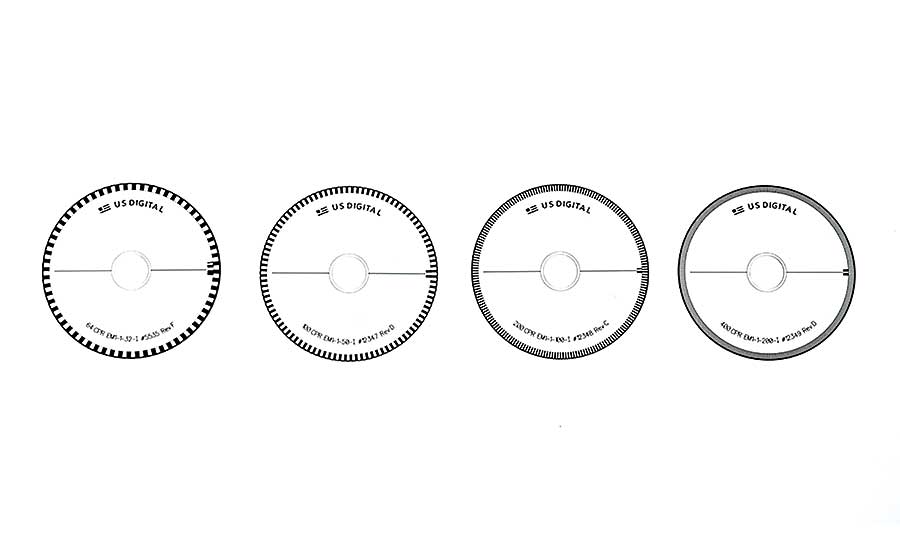
Resolution Accuracy And Precision Of Encoders 19 09 11 Assembly
Resolved Tms3f279d I D Like To Know About F279d S Pto Function C00 Microcontrollers Forum C00 Microcontrollers Ti E2e Support Forums



